Difference between revisions of "Orbit"
(→Key Stage 4) |
(→Key Stage 4) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
|} | |} | ||
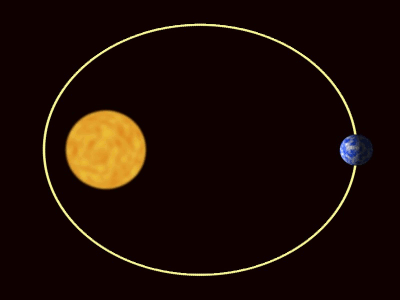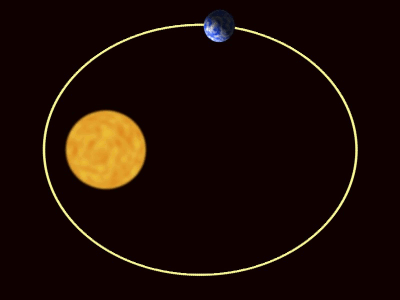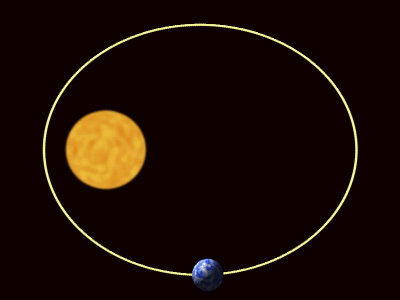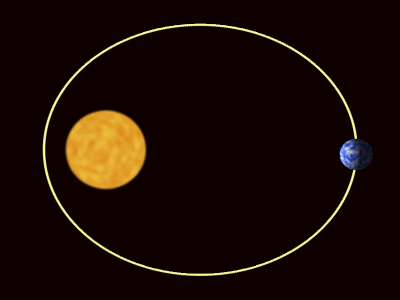
| − | + | :*Elliptical [[orbit]] - An [[orbit]] where the distance between the two [[object]]s changes. In this [[orbit]] the [[speed]] of the [[orbit]]ting [[object]] changes with the distance between the [[object]]s. The greater the distance the smaller the [[speed]]. | |
| − | :*Elliptical [[orbit]] | ||
Revision as of 13:03, 12 March 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
An Orbit is the path planet takes around a star and the path a moon takes around a planet.
| A Planet orbiting a Star. |
About Orbits
- An orbit is a roughly circular path, but can be stretched out into an oval shape.
- The Moon orbits the Earth. This means The Moon takes a circular path around the Earth.
- All the planets orbit The Sun. This means the planets take a circular path around The Sun.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
An Orbit is the path an asteroid, comet, planet or dwarf planet takes around a star and the path a moon takes around a planet.
About Orbits
- Moons orbit planets and planets orbit the stars due to gravity.
- Newton was the first person to realise that objects were held in orbit by gravity which he explained in his Universal Theory of Gravitation.
- Gravity is a constant force directed to the centre of a massive object.
- The Moon feels a force pulling it towards the centre of the Earth. The Earth feels a force equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to that of The Moon.
| The planets are pulled towards The Sun by gravity. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
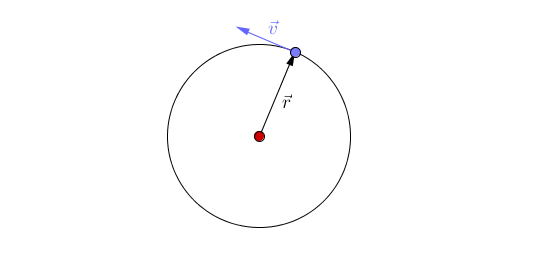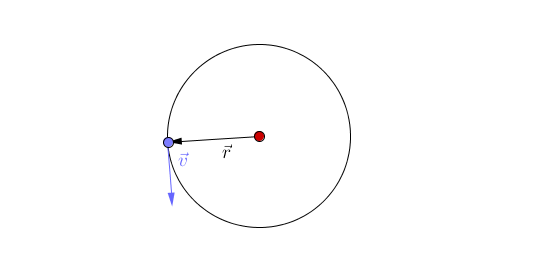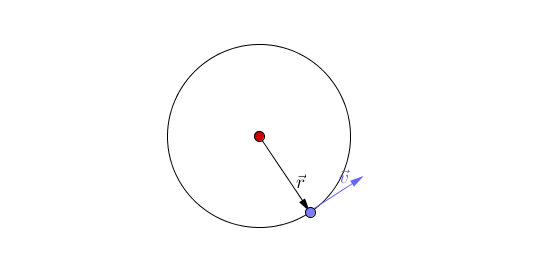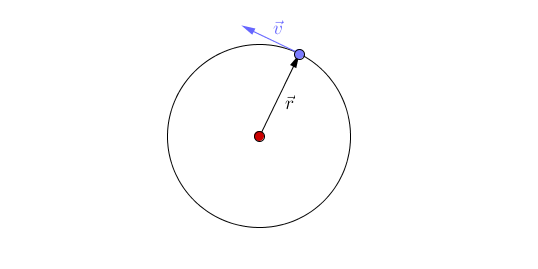
An orbit is the circular or elliptical path that an object takes a more massive object due to a force of attraction acting between them.
About Orbits
- Orbits are caused by a force of attraction between two objects acting towards their centres.
- Planets orbit Stars due to the force of gravity.
- There are two types of orbit you should know:
| This animation shows acceleration due to the changing direction of a circular orbit of the blue object around the red object. A circular orbit is one of constant radius. |