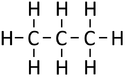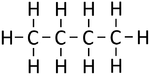Difference between revisions of "Alkane"
(→Examples) |
(→Examples) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" | |
| style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Methane''' | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Methane''' | ||
| style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Ethane | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Ethane | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Butane''' | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Butane''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" |[[Chemical Formula]] (C<sub>n</sub>H<sub>2n+2</sub>) |
| style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>4</sub> | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>4</sub> | ||
| style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>6</sub> | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>6</sub> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>10</sub> | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>10</sub> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" |[[Structural Formula]] |
| style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>4</sub> | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>4</sub> | ||
| style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>3</sub> | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>3</sub> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>3</sub> | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>3</sub> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" |[[Structural Diagram]] |
|[[File:StructuralDiagramMethane.png|center|75px]] | |[[File:StructuralDiagramMethane.png|center|75px]] | ||
|[[File:StructuralDiagramEthane.png|center|100px]] | |[[File:StructuralDiagramEthane.png|center|100px]] | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
|[[File:StructuralDiagramButane.png|center|150px]] | |[[File:StructuralDiagramButane.png|center|150px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:75px; text-align:center;" |[[Ball and Stick Model]] |
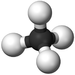
|[[File:BallandStickMethane.png|center|75px]] | |[[File:BallandStickMethane.png|center|75px]] | ||
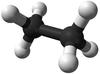
|[[File:BallandStickEthane.png|center|100px]] | |[[File:BallandStickEthane.png|center|100px]] | ||
Revision as of 16:52, 17 January 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
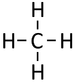
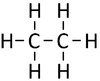
Alkanes are the simplest form of hydrocarbon compounds with no double bonds and the general formula; CnH2n+2
About Alkanes
- Alkanes are a homologous series of hydrocarbon compounds.
- The functional group of the Alkanes is the single bonds between the Carbon atoms and between the Carbon and Hydrogen atoms.
- Alkanes are long chains of Carbon atoms covalently bonded together with single bonds and Hydrogen atoms taking the remaining bonds.
Examples
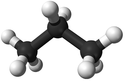
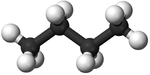
| Methane | Ethane | Propane | Butane | |
| Chemical Formula (CnH2n+2) | CH4 | C2H6 | C3H8 | C4H10 |
| Structural Formula | CH4 | CH3CH3 | CH3CH2CH3 | CH3CH2CH2CH3 |
| Structural Diagram | ||||
| Ball and Stick Model |