Key Stage 4
Meaning
The motor effect is the force on a current carrying wire in a magnetic field.
About The Motor Effect
- When an a wire has an electrical current it has a magnetic field. If this wire is in the presence of an external magnetic field the two fields will interact causing a force.
- The magnitude of the force depends upon:
- The Current - The greater the current the greater the force.
- The Magnetic Field - The greater the strength of magnetic field the greater the force.
- The force on a current carrying wire is at right angles to both the current and the magnetic field.
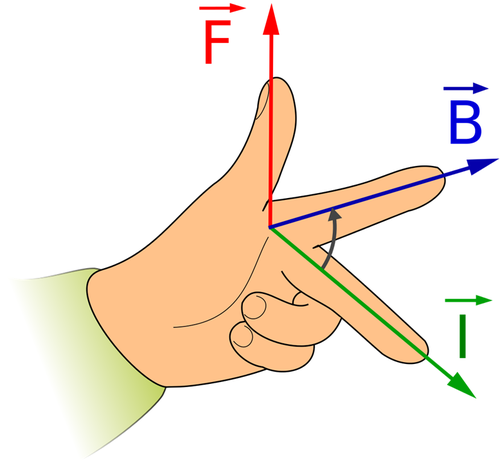
- Fleming's Left Hand Rule can be used to find the direction of the force.
|
\(\overrightarrow{B}\): First finger field. \(\overrightarrow{I}\): Second finger current. \(\overrightarrow{F}\): The force. |
Equation
Force = (Magnetic Flux Density) x (Current) x (Length)
\(F = BIl\)
Where\[B\] = The Magnetic Flux Density (strength of magnetic field).
\(I\) = The Electrical Current through the wire.
\(l\) = The length of wire inside the magnetic field.
\(F\) = The force on the wire.