Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A monomer is as small molecule that can bond with other molecules to form a polymer.
About Monomers
Foundation
There are some monomers that you may know:
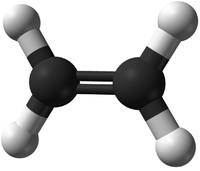
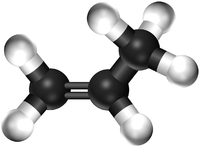
- Ethene - This monomer comes together in an Addition Polymerisation to form the polymer; Polythene.
- Propene - This monomer comes together in an Addition Polymerisation to form the polymer; Polypropene.
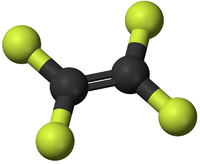
- TetraFluoroEthene - This monomer comes together in an Addition Polymerisation to form the polymer; PolyTetraFluoroEthene.
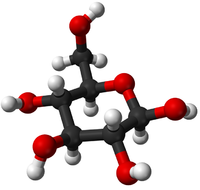
- Glucose - This monomer forms the polymers; Starch and Glycogen.
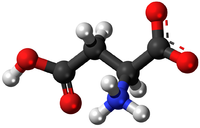
- Amino Acids - This monomer forms the polymers known as Proteins.
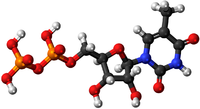
- Nucleotides - This monomer forms the polymer; DNA.
Higher
- Glucose - This monomer comes together in a Condensation Polymerisation to form the polymers; Starch and Glycogen.
- Amino Acids - This monomer comes together in a Condensation Polymerisation to form the polymers known as Proteins.
- Nucleotides - This monomer comes together in a Condensation Polymerisation to form the polymer; DNA.
Examples
| Glucose | Amino Acid | Nucleotide |
| Ethene | Propene | Tetrafluoroethene |
References
AQA
- Monomer, pages 74-5, 246-9, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Monomers, page 158, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Monomers, pages 168-169, 224, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Monomers, pages 187, 263, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Monomers, pages 236, 237, 241, 244, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Monomers, pages 80, 83, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Monomers; of addition polymers, page 188, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Monomers; of condensation polymers, page 191, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Monomers, page 12, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Monomers, pages 12, 187, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Monomers, pages 288-292, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Monomers, pages 43, 184, 203, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Monomers, pages 99, 100, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel