Difference between revisions of "Feynman Diagram"
(→Examples) |
(→Examples) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|- | |- | ||
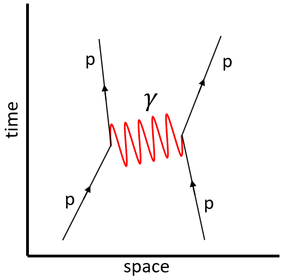
| style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |This '''Feynman diagram''' shows the [[Electromagnetic Interaction|electromagnetic interaction]] between two [[proton]]s via the virtual [[photon]]. | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |This '''Feynman diagram''' shows the [[Electromagnetic Interaction|electromagnetic interaction]] between two [[proton]]s via the virtual [[photon]]. | ||
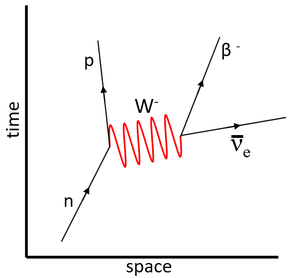
| − | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |This '''Feynman diagram''' shows the [[Weak Interaction|weak interaction]] in which a [[neutron]] [[Radioactive Decay|decays]] into a [[proton]]. | + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |This '''Feynman diagram''' shows the [[Weak Nuclear Interaction|weak interaction]] in which a [[neutron]] [[Radioactive Decay|decays]] into a [[proton]]. |
<math>n \rightarrow p + \beta^- + \bar\nu_e</math> | <math>n \rightarrow p + \beta^- + \bar\nu_e</math> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
|[[File:FeynmanDiagramUpDecay.png|center|300px]] | |[[File:FeynmanDiagramUpDecay.png|center|300px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
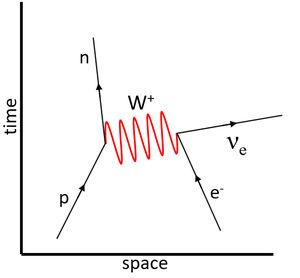
| − | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |This '''Feynman diagram''' shows the [[Weak Interaction|weak interaction]] in which a [[proton]] [[Electron Capture|captures]] an [[electron]] to become a [[neutron]]. | + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |This '''Feynman diagram''' shows the [[Weak Nuclear Interaction|weak interaction]] in which a [[proton]] [[Electron Capture|captures]] an [[electron]] to become a [[neutron]]. |
<math>p + \beta^- \rightarrow n + \nu_e</math> | <math>p + \beta^- \rightarrow n + \nu_e</math> | ||
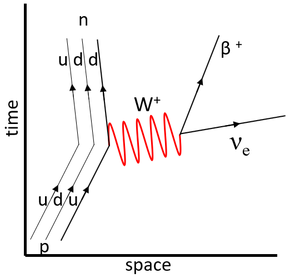
| − | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |This '''Feynman diagram''' shows the [[Weak Interaction|weak interaction]] in which an [[up-quark]] [[Radioactive Decay|decays]] into a [[down-quark]], which is observed as a [[proton]] [[Radioactive Decay|decaying]] into a [[neutron]] via [[Beta Particle|beta]] emission. | + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |This '''Feynman diagram''' shows the [[Weak Nuclear Interaction|weak interaction]] in which an [[up-quark]] [[Radioactive Decay|decays]] into a [[down-quark]], which is observed as a [[proton]] [[Radioactive Decay|decaying]] into a [[neutron]] via [[Beta Particle|beta]] emission. |
<math>u \rightarrow d + \beta^+ + \nu_e</math> | <math>u \rightarrow d + \beta^+ + \nu_e</math> | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 18:23, 31 July 2019
Key Stage 5
Meaning
A Feynman diagram is a type of graph used to represent the interactions between subatomic particles.
About Feynman Diagrams
- Feynman diagrams have time on the y-axis and space on the z-axis.
- Feynman diagrams are used to simplify complex equations used to represent subatomic particle interactions.
Examples
| This Feynman diagram shows the electromagnetic interaction between two protons via the virtual photon. | This Feynman diagram shows the weak interaction in which a neutron decays into a proton.
\(n \rightarrow p + \beta^- + \bar\nu_e\) |
| This Feynman diagram shows the weak interaction in which a proton captures an electron to become a neutron.
\(p + \beta^- \rightarrow n + \nu_e\) |
This Feynman diagram shows the weak interaction in which an up-quark decays into a down-quark, which is observed as a proton decaying into a neutron via beta emission.
\(u \rightarrow d + \beta^+ + \nu_e\) |