Key Stage 4
Meaning
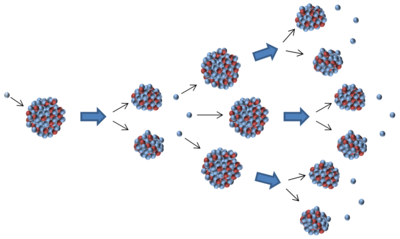
A nuclear chain reaction is when the neutrons released from one nuclear fission event triggers one or more other nuclear fission event.
About Nuclear Chain Reactions
- For a nuclear chain reaction to occur each nuclear fission event must cause the release of at least 1 neutron which can go on to cause a second fission event.
- In a nuclear reactor on average 1 neutron from each fission event goes on to cause one more fission event. This results in a constant release of energy.
- During nuclear fission the neutrons produced usually have too much energy to be captured by the nucleus of another atom, so they must be slowed down by a moderator to a lower energy in order for a chain reaction to occur.
- Neutrons with the right amount of energy to be captured are called thermal neutrons because they have a similar energy to molecules in the air at room temperature.
- A nuclear chain reaction can only happen if enough thermal neutrons are produced from the fission events.
| The neutrons released from one fission event go on to cause at least one other fission event in a chain reaction. |