Key Stage 5
Meaning
The weak nuclear interaction is the mechanism governing how hadrons and leptons affect one another.
About The Weak Nuclear Interaction
- The weak nuclear interaction is one of the 4 fundamental interactions governing how subatomic particless affect one another.
- The weak nuclear interaction causes the decay of particles into other, more stable, subatomic particless.
- The weak nuclear interaction can allow neutrons to decay into protons.
- The weak nuclear interaction is mediated by the W-boson and Z-boson.
- The effective range of the weak nuclear interaction is smaller than the diameter of a proton.
Examples
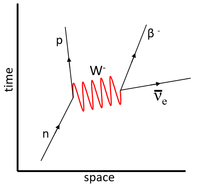
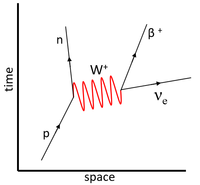
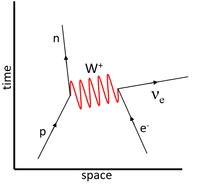
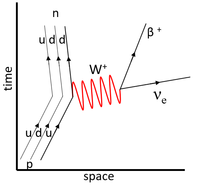
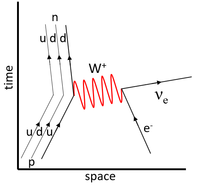
| This Feynman Diagram shows the weak interaction in which a neutron decays into a proton. | This Feynman Diagram shows the weak interaction in which a proton decays into a neutron via positron emission. | This Feynman Diagram shows the weak interaction in which a proton captures an electron to become a neutron. |
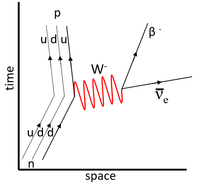
| This Feynman Diagram shows the weak interaction in which a down-quark decays into an up-quark. This appears as a neutron becoming a proton, electron and an antielectron-neutrino. | This Feynman Diagram shows the weak interaction in which an up-quark decays into a down-quark via positron emission. This appears as a proton becoming a neutron, positron and electron-neutrino. | This Feynman Diagram shows the weak interaction in which an up-quark captures an electron to become a neutron. This appears as a ground state electron becoming an electron-neutrino while a proton becomes a neutron. |