Inversely Proportional
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
When two variables are inversely proportional when one variable gets larger, the other variable gets smaller.
About Inverse Proportionality
- A scatter graph showing an inversely proportional relationship has a curved gradient.
- On an inversely proportional scatter graph when one variable increases, the other decreases but the change is not constant.
- The line of best fit on an inversely proportional graph will not cross either axis.
Examples
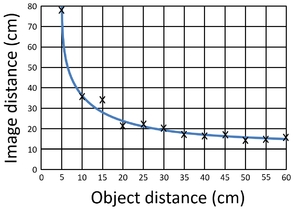
| This scatter graph shows that x is inversely proportional to y; as the magnitude of x increases the magnitude of y decreases. | This scatter graph of Image Distance against Object Distance of a Lens begins with a steep negative gradient which becomes more shallow until the gradient is almost zero. The relationship is inversely proportional. |
References
AQA
- Inverse proportionality, page 164, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Inverse proportionality, pages 114, 196, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA