Difference between revisions of "Pathogenic Bacteria"
(→Examples) |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
|[[File:BacteriaDiagram2.png|center|400px]] | |[[File:BacteriaDiagram2.png|center|400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
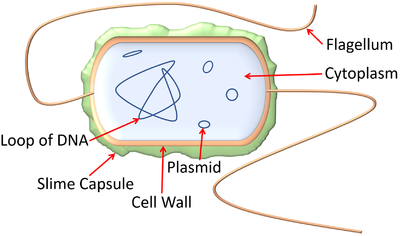
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] showing the features of | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] showing the features of an [[E.coli]] '''bacterium'''. |
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:03, 6 June 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A magnified image of several bacteria.
A pathogenic bacteria are bacteria which cause disease.
About Pathogenic Bacteria
- When a pathogenic bacteria enters the body it divides quickly making millions of copies of itself.
- Pathogenic bacteria make you feel ill because they release toxins into the body.
- Some pathogenic bacteria have a tail called a flagellum.
- Some pathogenic bacteria are encased in a slime capsule which protects them from phagocytes and some toxic chemicals.
- Bacteria are prokaryotes so they do not have a nucleus, mitochondria or chloroplasts.
| A diagram showing the features of an E.coli bacterium. |
Examples
- Cholera is a pathogenic bacteria spread in the water supply.
- E.coli is a pathogenic bacteria found in meat.
- Salmonella is a pathogenic bacteria found particularly in raw chicken meat but can be spread to other foods through contact.
- Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted pathogenic bacteria which is spread in the body fluids of organisms.