Difference between revisions of "Electrical Resistance"
| (20 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
===About Resistance=== | ===About Resistance=== | ||
| − | : The [[SI Unit|unit]] of '''resistance''' is the [[Ohm]] ( | + | : The [[SI Unit|unit]] of '''resistance''' is the [[Ohm]] (Ω). |
: '''Resistance''' cannot be directly [[measure]]d. '''Resistance''' must be calculated by dividing the [[Potential Difference]] by the [[Electrical Current|Current]]. | : '''Resistance''' cannot be directly [[measure]]d. '''Resistance''' must be calculated by dividing the [[Potential Difference]] by the [[Electrical Current|Current]]. | ||
: [[Electrical Conductor|Conductors]] have a low '''resistance''' and [[Electrical Insulator|insulator]]s have a high '''resistance'''. | : [[Electrical Conductor|Conductors]] have a low '''resistance''' and [[Electrical Insulator|insulator]]s have a high '''resistance'''. | ||
===Equation=== | ===Equation=== | ||
| − | + | '''Resistance''' = (Potential Difference)/(Current) | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <math>R = \frac{V}{I}</math> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Where | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R</math> = '''Resistance''' of a [[Electrical Component|component]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V</math> = The [[Potential Difference]] across the [[Electrical Component|component]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I</math> = The [[Electrical Current|current]] through the [[Electrical Component|component]]. | ||
===Example Calculations=== | ===Example Calculations=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''A student [[measure]]s a [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] of | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''A student [[measure]]s a [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] of 5V across a [[component]] and a [[Electrical Current|current]] of 0.1A. Calculate the resistance.''' |
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''A [[Electrical Bulb|bulb]] has a [[Electrical Current|current]] of | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''A [[Electrical Bulb|bulb]] has a [[Electrical Current|current]] of 200mA passing through it and a [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] of 12V across it. Calculate the resistance of the [[Electrical Bulb|bulb]].''' |
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Calculate the resistance of a [[buzzer]] connected in [[Series Circuit|series]] to a | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Calculate the resistance of a [[buzzer]] connected in [[Series Circuit|series]] to a 6V [[battery]] with an [[ammeter]] reading of 10mA.''' |
|- | |- | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| − | + | Potential Difference = 5V | |
| − | + | Current = 0.1A | |
| − | <math> | + | <math>R = \frac{V}{I}</math> |
| − | <math> | + | <math>R = \frac{5}{0.1}</math> |
| − | <math> | + | <math> R = 50 \Omega</math> |
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| − | + | Potential Difference = 12V | |
| − | + | Current = 200mA = 0.2A | |
| − | <math> | + | <math>R = \frac{V}{I}</math> |
| − | <math> | + | <math>R = \frac{12}{0.2}</math> |
| − | <math> | + | <math> R = 60 \Omega</math> |
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| − | + | Potential Difference = 6V | |
| + | |||
| + | Current = 10mA = 0.01A | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R = \frac{V}{I}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R = \frac{6}{0.01}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> R = 600 \Omega</math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | '''Resistance''' is the [[ratio]] of [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] to [[Electrical Current|current]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Resistance=== | ||
| + | : The [[SI Unit|unit]] of '''resistance''' is the [[Ohm]] (Ω). | ||
| + | : '''Resistance''' cannot be directly [[measure]]d. '''Resistance''' must be calculated by dividing the [[Potential Difference]] by the [[Electrical Current|Current]]. | ||
| + | : [[Electrical Conductor|Conductors]] have a low '''resistance''' and [[Electrical Insulator|insulator]]s have a high '''resistance'''. | ||
| + | : '''Resistance''' in a [[wire]] is caused by [[electron]]s colliding with [[Positive Ion|positive ion]]s in the [[metal]] [[lattice]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ResistanceCause.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
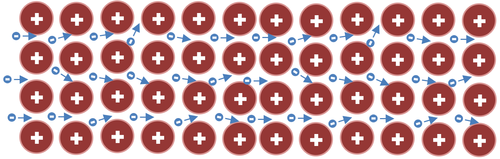
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows [[electron]]s moving past the [[Positive Ion|positive ions]] in a [[metal]] [[lattice]]. As they move some of them collide with the [[Positive Ion|positive ions]] in the [[lattice]] which is acts as a '''resistance''' to an [[Electrical Current|electrical current]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | : The higher the [[temperature]] of a [[Electrical Conductor|conductor]] the greater the '''resistance''' of that [[Electrical Conductor|conductor]]. This is due to the [[metal]] [[ion]]s vibrating faster at higher [[temperature]]s which makes [[electron]]s more likely to collide with the [[ion]]s as they pass through the [[Electrical Conductor|conductor]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Equation=== | ||
| + | '''Resistance''' = (Potential Difference)/(Current) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R = \frac{V}{I}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R</math> = '''Resistance''' of a [[Electrical Component|component]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V</math> = The [[Potential Difference]] across the [[Electrical Component|component]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I</math> = The [[Electrical Current|current]] through the [[Electrical Component|component]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Example Calculations=== | ||
| + | ====Finding Resistance from Current and Potential Difference==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |'''A student [[measure]]s a [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] of 5.9V across a [[component]] and a [[Electrical Current|current]] of 0.11A. Calculate the resistance correct to two [[Significant Figures|significant figures]].''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |'''Calculate the resistance of a [[buzzer]] connected in [[Series Circuit|series]] to a 9V [[battery]] with an [[ammeter]] reading of 23mA correct to two [[Significant Figures|significant figures]].''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities in correct [[unit]]s.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Potential Difference = 5.9V | ||
| + | |||
| + | Current = 0.11A | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities in correct [[unit]]s.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Potential Difference = 9V | ||
| + | |||
| + | Current = 23mA = 23x10<sup>-3</sup>A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers into the [[equation]] and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R = \frac{V}{I}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R = \frac{5.9}{0.11}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> R = 53.635 \Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> R \approx 54\Omega</math> | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers into the [[equation]] and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R = \frac{V}{I}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R = \frac{9}{23\times10^{-3}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> R = 391.304 \Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> R \approx 390 \Omega</math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Finding Current from Potential Difference and Resistance==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] of 9.9V is placed across an 19 Ohm [[Electrical Resistor|resistor]]. Calculate the '''current''' flowing through the [[Electrical Resistor|resistor]] correct to two [[Significant Figures|significant figures]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A toaster has a [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] of 27 Ohms is plugged into the [[Mains Electricity|mains]] which has a [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] of 230V. Calculate the current flowing through the toaster correct to two [[Significant Figures|significant figures]]. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities in correct [[unit]]s.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | V = 9.9V | ||
| + | |||
| + | R = 19Ω | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities in correct [[unit]]s.''' | ||
| + | V = 230V | ||
| + | |||
| + | R = 27Ω | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers and [[Evaluate (Maths)|evaluate]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R = \frac{V}{I}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>19=\frac{9.9}{I}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers and [[Evaluate (Maths)|evaluate]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R = \frac{V}{I}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>27=\frac{230}{R}</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''3. [[Rearrange (Maths)|Rearrange]] the equation and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I=\frac{9.9}{19}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I=0.52105A</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I\approx0.52A</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''3. [[Rearrange (Maths)|Rearrange]] the equation and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I=\frac{230}{27}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I=8.519A</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I\approx8.5A</math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Finding Potential Difference from Current and Resistance==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:center;" |A '''current''' of 55mA flows through a [[Electrical Component|component]] with a [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] of 93 Ohms. Calculate the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across this [[Electrical Component|component]] correct to two [[Significant Figures|significant figures]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:center;" |A 22kΩ [[Electrical Resistor|resistor]] has a '''current''' flowing through it of 6mA. Calculate the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across the [[Electrical Resistor|resistor]] correct to two [[Significant Figures|significant figures]]. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities in correct [[unit]]s.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | I = 55mA = 55x10<sup>-3</sup>A | ||
| + | |||
| + | R = 93Ω | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities in correct [[unit]]s.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | I = 6mA = 6x10<sup>-3</sup>A | ||
| + | |||
| + | R = 22kΩ = 22x10<sup>3</sup>Ω | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers and [[Evaluate (Maths)|evaluate]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R = \frac{V}{I}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>93=\frac{V}{55 \times 10^{-3}}</math> | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers and [[Evaluate (Maths)|evaluate]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R = \frac{V}{I}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>22 \times 10^3=\frac{V}{6 \times 10^{-3}}</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''3. [[Rearrange (Maths)|Rearrange]] the equation and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| − | + | <math>V= 55 \times 10^{-3} \times 93</math> | |
| − | <math> | + | <math>V= 5.115V</math> |
| − | <math> | + | <math>V\approx5.1V</math> |
| − | + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''3. [[Rearrange (Maths)|Rearrange]] the equation and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | |
| − | + | <math>V= 6 \times 10^{-3} \times 22 \times 10^3</math> | |
| + | |||
| + | <math>V= 132V</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V\approx130V</math> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Resistance (electrical), page 63, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Resistance (electrical), page 65, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10246 ''Resistance (electrical), pages 180-184, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac384 ''Resistance (electrical), pages 24-30, 32, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10247 ''Resistance (electrical); in parallel circuits, pages 186, 187, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac385 ''Resistance (electrical); in parallel circuits, pages 29, 30, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Resistance (electrical); in parallel, pages 74, 77-79, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Resistance (electrical); in parallel, pages 76, 79-81, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10248 ''Resistance (electrical); in series circuits, pages 185, 187, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac386 ''Resistance (electrical); in series circuits, pages 28, 30, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Resistance (electrical); in series, pages 70, 77, 78, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Resistance (electrical); in series, pages 72, 79, 80, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Resistance (electrical); investigating, pages 64, 77-79, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Resistance (electrical); investigating, pages 66, 79-81, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Resistance (electrical); of diodes, page 66, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Resistance (electrical); of diodes, page 68, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Resistance (electrical); of filament lamps, page 66, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Resistance (electrical); of filament lamps, page 68, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Resistance (electrical); of LDRs, page 80, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Resistance (electrical); of LDRs, page 82, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Resistance (electrical); of resistors, pages 65, 66, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Resistance (electrical); of resistors, pages 67, 68, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Resistance (electrical); of thermistors, pages 80, 81, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Resistance (electrical); of thermistors, pages 82, 83, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10249 ''Resistance (electrical); wire length, page 182, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:07, 12 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Resistance is a description of how difficult it is to increase the current through a conductor when increasing the potential difference.
About Resistance
- The unit of resistance is the Ohm (Ω).
- Resistance cannot be directly measured. Resistance must be calculated by dividing the Potential Difference by the Current.
- Conductors have a low resistance and insulators have a high resistance.
Equation
Resistance = (Potential Difference)/(Current)
\(R = \frac{V}{I}\)
Where
\(R\) = Resistance of a component.
\(V\) = The Potential Difference across the component.
\(I\) = The current through the component.
Example Calculations
| A student measures a potential difference of 5V across a component and a current of 0.1A. Calculate the resistance. | A bulb has a current of 200mA passing through it and a potential difference of 12V across it. Calculate the resistance of the bulb. | Calculate the resistance of a buzzer connected in series to a 6V battery with an ammeter reading of 10mA. |
|
Potential Difference = 5V Current = 0.1A \(R = \frac{V}{I}\) \(R = \frac{5}{0.1}\) \( R = 50 \Omega\) |
Potential Difference = 12V Current = 200mA = 0.2A \(R = \frac{V}{I}\) \(R = \frac{12}{0.2}\) \( R = 60 \Omega\) |
Potential Difference = 6V Current = 10mA = 0.01A \(R = \frac{V}{I}\) \(R = \frac{6}{0.01}\) \( R = 600 \Omega\) |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Resistance is the ratio of potential difference to current.
About Resistance
- The unit of resistance is the Ohm (Ω).
- Resistance cannot be directly measured. Resistance must be calculated by dividing the Potential Difference by the Current.
- Conductors have a low resistance and insulators have a high resistance.
- Resistance in a wire is caused by electrons colliding with positive ions in the metal lattice.
| This diagram shows electrons moving past the positive ions in a metal lattice. As they move some of them collide with the positive ions in the lattice which is acts as a resistance to an electrical current. |
- The higher the temperature of a conductor the greater the resistance of that conductor. This is due to the metal ions vibrating faster at higher temperatures which makes electrons more likely to collide with the ions as they pass through the conductor.
Equation
Resistance = (Potential Difference)/(Current)
\(R = \frac{V}{I}\)
Where
\(R\) = Resistance of a component.
\(V\) = The Potential Difference across the component.
\(I\) = The current through the component.
Example Calculations
Finding Resistance from Current and Potential Difference
| A student measures a potential difference of 5.9V across a component and a current of 0.11A. Calculate the resistance correct to two significant figures. | Calculate the resistance of a buzzer connected in series to a 9V battery with an ammeter reading of 23mA correct to two significant figures. |
| 1. State the known quantities in correct units.
Potential Difference = 5.9V Current = 0.11A |
1. State the known quantities in correct units.
Potential Difference = 9V Current = 23mA = 23x10-3A |
| 2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
\(R = \frac{V}{I}\) \(R = \frac{5.9}{0.11}\) \( R = 53.635 \Omega\) \( R \approx 54\Omega\) |
2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
\(R = \frac{V}{I}\) \(R = \frac{9}{23\times10^{-3}}\) \( R = 391.304 \Omega\) \( R \approx 390 \Omega\) |
Finding Current from Potential Difference and Resistance
| A potential difference of 9.9V is placed across an 19 Ohm resistor. Calculate the current flowing through the resistor correct to two significant figures. | A toaster has a resistance of 27 Ohms is plugged into the mains which has a potential difference of 230V. Calculate the current flowing through the toaster correct to two significant figures. |
| 1. State the known quantities in correct units.
V = 9.9V R = 19Ω |
1. State the known quantities in correct units.
V = 230V R = 27Ω |
| 2. Substitute the numbers and evaluate.
\(R = \frac{V}{I}\) \(19=\frac{9.9}{I}\) |
2. Substitute the numbers and evaluate.
\(R = \frac{V}{I}\) \(27=\frac{230}{R}\) |
| 3. Rearrange the equation and solve.
\(I=\frac{9.9}{19}\) \(I=0.52105A\) \(I\approx0.52A\) |
3. Rearrange the equation and solve.
\(I=\frac{230}{27}\) \(I=8.519A\) \(I\approx8.5A\) |
Finding Potential Difference from Current and Resistance
| A current of 55mA flows through a component with a resistance of 93 Ohms. Calculate the potential difference across this component correct to two significant figures. | A 22kΩ resistor has a current flowing through it of 6mA. Calculate the potential difference across the resistor correct to two significant figures. |
| 1. State the known quantities in correct units.
I = 55mA = 55x10-3A R = 93Ω |
1. State the known quantities in correct units.
I = 6mA = 6x10-3A R = 22kΩ = 22x103Ω |
| 2. Substitute the numbers and evaluate.
\(R = \frac{V}{I}\) \(93=\frac{V}{55 \times 10^{-3}}\) |
2. Substitute the numbers and evaluate.
\(R = \frac{V}{I}\) \(22 \times 10^3=\frac{V}{6 \times 10^{-3}}\) |
| 3. Rearrange the equation and solve.
\(V= 55 \times 10^{-3} \times 93\) \(V= 5.115V\) \(V\approx5.1V\) |
3. Rearrange the equation and solve.
\(V= 6 \times 10^{-3} \times 22 \times 10^3\) \(V= 132V\) \(V\approx130V\) |
References
AQA
- Resistance (electrical), page 63, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical), page 65, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical), pages 180-184, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical), pages 24-30, 32, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); in parallel circuits, pages 186, 187, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); in parallel circuits, pages 29, 30, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); in parallel, pages 74, 77-79, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); in parallel, pages 76, 79-81, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); in series circuits, pages 185, 187, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); in series circuits, pages 28, 30, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); in series, pages 70, 77, 78, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); in series, pages 72, 79, 80, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); investigating, pages 64, 77-79, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); investigating, pages 66, 79-81, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); of diodes, page 66, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); of diodes, page 68, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); of filament lamps, page 66, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); of filament lamps, page 68, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); of LDRs, page 80, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); of LDRs, page 82, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); of resistors, pages 65, 66, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); of resistors, pages 67, 68, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); of thermistors, pages 80, 81, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); of thermistors, pages 82, 83, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Resistance (electrical); wire length, page 182, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA