Difference between revisions of "Condensation Polymerisation"
(→Forming Polyesters) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
: '''Condensation polymerisation''' [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]]s are called '''condensation''' [[Chemical Reaction|reactions]] because they usually [[product|produce]] [[Water]], but they may also [[Product|produce]] other small [[molecule]]s such as HCl. | : '''Condensation polymerisation''' [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]]s are called '''condensation''' [[Chemical Reaction|reactions]] because they usually [[product|produce]] [[Water]], but they may also [[Product|produce]] other small [[molecule]]s such as HCl. | ||
: '''Condensation polymerisation''' [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]]s happen commonly in biological [[organism]]s. | : '''Condensation polymerisation''' [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]]s happen commonly in biological [[organism]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
====Forming Polyesters==== | ====Forming Polyesters==== | ||
: '''Condensation polymerisation''' [[Chemical Reaction|reactions]] which [[product|produce]] [[Water]] can happen when one end of a [[molecule]] carries an -OH [[Functional Group|group]] while the other end carries a -COOH [[Functional Group|group]]. These [[Chemical Reaction|react]] together joining the [[molecule]]s forming a [[Polyester]]. | : '''Condensation polymerisation''' [[Chemical Reaction|reactions]] which [[product|produce]] [[Water]] can happen when one end of a [[molecule]] carries an -OH [[Functional Group|group]] while the other end carries a -COOH [[Functional Group|group]]. These [[Chemical Reaction|react]] together joining the [[molecule]]s forming a [[Polyester]]. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 19: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |Ethandioate and Ethandiol can [[Chemical Reaction|react]] together in a '''Condensation Polymerisation'''. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |Ethandioate and Ethandiol can [[Chemical Reaction|react]] together in a '''Condensation Polymerisation'''. | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Polyester]] is formed. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Polyester]] is formed along with [[Water]]. |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 27: | Line 29: | ||
n x Glucose → Starch + Water | n x Glucose → Starch + Water | ||
| − | Where 'n' represents an | + | Where 'n' represents an integer. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 34: | Line 36: | ||
|[[File:StructuralDiagramStarch.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:StructuralDiagramStarch.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Glucose]] [[molecule]]s [[Chemical Reaction|react]] together in a '''condensation polymerisation''' [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]]. |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Starch]] is formed along with [[Water]]. |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
====Forming Proteins==== | ====Forming Proteins==== | ||
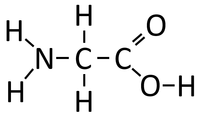
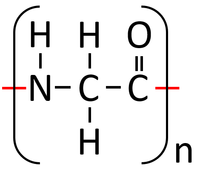
| − | : '''Condensation polymerisation''' [[Chemical Reaction|reactions]] of [[Peptide]]s ([[Amino Acid]]s) [[product|produce]] [[Polypeptide]]s ([[ | + | : '''Condensation polymerisation''' [[Chemical Reaction|reactions]] of [[Peptide]]s ([[Amino Acid]]s) [[product|produce]] [[Polypeptide]]s ([[Protein]]s) and [[Water]]. |
: Each [[Amino Acid]] has an NH<sub>2</sub> [[Functional Group|group]] which acts as a [[base]] and an -COOH [[Functional Group|group]] which acts as an [[acid]]. These [[Functional Group|functional groups]] [[Chemical Reaction|react]] to [[Product|produce]] [[Polypeptide]]s and [[Water]]. | : Each [[Amino Acid]] has an NH<sub>2</sub> [[Functional Group|group]] which acts as a [[base]] and an -COOH [[Functional Group|group]] which acts as an [[acid]]. These [[Functional Group|functional groups]] [[Chemical Reaction|react]] to [[Product|produce]] [[Polypeptide]]s and [[Water]]. | ||
n x Peptides → Polypeptide + Water | n x Peptides → Polypeptide + Water | ||
| Line 45: | Line 48: | ||
<chem>nH2NCH2COOH -> (-HNCH2CO-) + nH2O</chem> | <chem>nH2NCH2COOH -> (-HNCH2CO-) + nH2O</chem> | ||
| − | Where 'n' represents an | + | Where 'n' represents an integer. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 53: | Line 56: | ||
|[[File:StructuralDiagramPolyglycine.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:StructuralDiagramPolyglycine.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Glycine]] [[molecule]]s [[Chemical Reaction|react]] together in a '''condensation polymerisation''' [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]]. |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Polypeptide]] ([[Protein]]) is formed along with [[Water]]. In reality [[Polypeptide]]s are made of many different [[Peptide]]s ([[Amino Acid]]s) rather than the same one repeated. |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Condensation polymerisation, pages 188-189, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:21, 17 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4 Higher
Meaning
Condensation polymerisation is a reaction in which monomers combine to form polymers producing a H2O or HCl molecule for each addition of a monomer.
About Condensation Polymerisation
- Condensation polymerisation reactions are called condensation reactions because they usually produce Water, but they may also produce other small molecules such as HCl.
- Condensation polymerisation reactions happen commonly in biological organisms.
Examples
Forming Polyesters
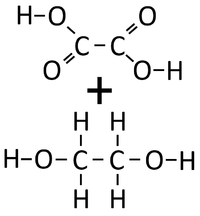
- Condensation polymerisation reactions which produce Water can happen when one end of a molecule carries an -OH group while the other end carries a -COOH group. These react together joining the molecules forming a Polyester.
- Condensation polymerisation reactions which produce Water can also happen when one molecule carries two -OH groups at either end of the molecule while the other molecule carries two -COOH groups. These two molecules react together joining the molecules forming a Polyester and producing Water.
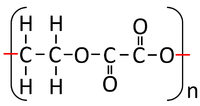
| Ethandioate and Ethandiol can react together in a Condensation Polymerisation. | A Polyester is formed along with Water. |
Forming Polysaccharides
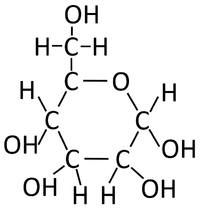
- The condensation polymerisation reaction of monosaccharides produces a polysaccharide and Water.
- The monosaccharide glucose can bond in a condensation polymersiation reaction to produce starch or glycogen.
n x Monosaccharides → Polysaccharide + Water
n x Glucose → Starch + Water
Where 'n' represents an integer.
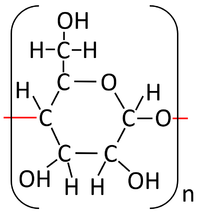
| Glucose molecules react together in a condensation polymerisation reaction. | Starch is formed along with Water. |
Forming Proteins
- Condensation polymerisation reactions of Peptides (Amino Acids) produce Polypeptides (Proteins) and Water.
- Each Amino Acid has an NH2 group which acts as a base and an -COOH group which acts as an acid. These functional groups react to produce Polypeptides and Water.
n x Peptides → Polypeptide + Water
<chem>nH2NCH2COOH -> (-HNCH2CO-) + nH2O</chem>
Where 'n' represents an integer.
| Glycine molecules react together in a condensation polymerisation reaction. | A Polypeptide (Protein) is formed along with Water. In reality Polypeptides are made of many different Peptides (Amino Acids) rather than the same one repeated. |