Difference between revisions of "Absorption Spectra"
| (7 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
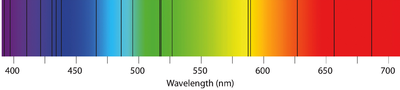
| − | [[File:AbsorptionSpectrum.png|right| | + | [[File:AbsorptionSpectrum.png|right|400px|thumb|The [[Absorption Spectra|absorption spectrum]] of several [[element]]s within one [[sample]].]] |
'''Absorption spectra''' are the specific [[wavelength]]s of [[light]] [[Absorb (Physics)|absorbed]] by the [[electron]]s in [[atom]]s as they gain [[energy]]. | '''Absorption spectra''' are the specific [[wavelength]]s of [[light]] [[Absorb (Physics)|absorbed]] by the [[electron]]s in [[atom]]s as they gain [[energy]]. | ||
| − | ===About | + | ===About Absorption Spectra=== |
| − | : An '''absorption spectrum''' is made by passing [[White Light|white light]] through a [[material]] or [[reflection|reflecting]] it off a [[material]] then sending it through a [[prism]] to separate the [[colour]]s. | + | : An '''absorption spectrum''' is made by passing [[White Light|white light]] through a [[material]] or [[reflection|reflecting]] it off a [[material]] then sending it through a [[Prism (Physics)|prism]] to separate the [[colour]]s. |
: The [[spectrum]] of [[White Light|white light]] is a continuous change of [[colour]]s with all [[wavelength]]s having the same [[intensity]]. | : The [[spectrum]] of [[White Light|white light]] is a continuous change of [[colour]]s with all [[wavelength]]s having the same [[intensity]]. | ||
: An '''absorption spectrum''' is a set of specific [[wavelength]]s with a low [[intensity]]. This appears as dark lines of of missing [[colour]] from the normal [[spectrum]] made by [[White Light|white light]]. | : An '''absorption spectrum''' is a set of specific [[wavelength]]s with a low [[intensity]]. This appears as dark lines of of missing [[colour]] from the normal [[spectrum]] made by [[White Light|white light]]. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
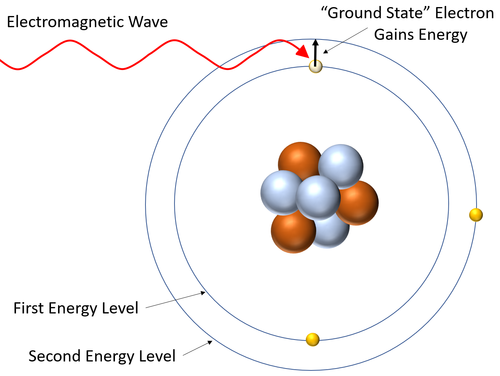
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows an [[electron]] gaining [[energy]] by [[Absorb (Physics)|absorbing]] an [[Electromagnetic Wave|electromagnetic wave]] and becoming [[excited]] (moving to a higher [[Energy Level|energy level]]). | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows an [[electron]] gaining [[energy]] by [[Absorb (Physics)|absorbing]] an [[Electromagnetic Wave|electromagnetic wave]] and becoming [[excited]] (moving to a higher [[Energy Level|energy level]]). | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Absorption; lines, page 111, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Absorption spectra, pages 191, 192, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Absorption spectrum, page 359, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Absorption spectrum, page 95, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Absorption spectrum, pages 178-179, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:06, 30 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Absorption spectra are the specific wavelengths of light absorbed by the electrons in atoms as they gain energy.
About Absorption Spectra
- An absorption spectrum is made by passing white light through a material or reflecting it off a material then sending it through a prism to separate the colours.
- The spectrum of white light is a continuous change of colours with all wavelengths having the same intensity.
- An absorption spectrum is a set of specific wavelengths with a low intensity. This appears as dark lines of of missing colour from the normal spectrum made by white light.
- A absorption spectrum is created when electrons absorb the energy from an electromagnetic wave and jump to a higher energy level in an atom. This removes that particular wavelength of electromagnetic wave white light being transmitted or reflected from that material.
- The wavelengths of electromagnetic wave depend on the energy difference between the energy levels in atoms.
| This diagram shows an electron gaining energy by absorbing an electromagnetic wave and becoming excited (moving to a higher energy level). |
References
AQA
Edexcel
- Absorption spectra, pages 191, 192, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Absorption spectrum, page 359, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Absorption spectrum, page 95, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel