Difference between revisions of "Electrical Heater"
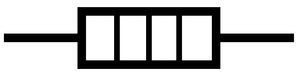
(Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== right|300px|thumb|The symbol for an '''electrical heater'''. A '''heater''' is a component in...") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
: '''Heaters''' are usually long lengths of [[wire]] which a high [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]]. | : '''Heaters''' are usually long lengths of [[wire]] which a high [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]]. | ||
: As a [[Electrical Current|current]] passes through a [[wire]] [[electron]]s in the [[Electrical Current|current]] [[collide]] with [[ion]]s in the [[metal]] [[lattice]] causing them to [[vibrate]]. This increases the [[temperature]] of the [[wire]]. | : As a [[Electrical Current|current]] passes through a [[wire]] [[electron]]s in the [[Electrical Current|current]] [[collide]] with [[ion]]s in the [[metal]] [[lattice]] causing them to [[vibrate]]. This increases the [[temperature]] of the [[wire]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Energy Transfers=== | ||
| + | : In an '''electrical heater''' [[Work Done#Work Done by Electricity|electrical work]] is done to [[heat]] an [[object]] or the surroundings. | ||
| + | : [[Energy]] is [[Energy Transfer|transferred]] into the [[Thermal Energy Store|thermal energy store]] of the '''heater'''. | ||
| + | : [[Energy]] is [[Energy Transfer|transferred]] by [[Thermal Conduction|thermal conduction]], [[convection]] and by [[radiation]] to the [[Thermal Energy Store|thermal energy store]] of the surroundings. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945679/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945679&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a2db42f7b4bdf10cafaafa3bb9120940 ''Electrical heaters, page 105, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:33, 5 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A heater is a component in a circuit which is heated when a current goes through it.
About Electrical Heaters
- Heaters are usually long lengths of wire which a high resistance.
- As a current passes through a wire electrons in the current collide with ions in the metal lattice causing them to vibrate. This increases the temperature of the wire.
Energy Transfers
- In an electrical heater electrical work is done to heat an object or the surroundings.
- Energy is transferred into the thermal energy store of the heater.
- Energy is transferred by thermal conduction, convection and by radiation to the thermal energy store of the surroundings.