Difference between revisions of "Electromagnet"
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
===Compared to a Bar Magnet=== | ===Compared to a Bar Magnet=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |'''Advantages of an Electromagnet over a Bar Magnet''' |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |'''Disadvantages of an Electromagnet compared to a Bar Magnet''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" | |
Changing the [[Electrical Current|current]] can change the strength of an [[electromagnet]]. | Changing the [[Electrical Current|current]] can change the strength of an [[electromagnet]]. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
The direction of the [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] can be changed in an [[electromagnet]] by changing the direction of the [[Electrical Current|current]]. | The direction of the [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] can be changed in an [[electromagnet]] by changing the direction of the [[Electrical Current|current]]. | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" | |
[[Electromagnet]]s require a source of power to work. | [[Electromagnet]]s require a source of power to work. | ||
[[Electromagnet]]s increase in [[temperature]] as they are used. | [[Electromagnet]]s increase in [[temperature]] as they are used. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | An [[electromagnet]] is a [[magnet]] made from a [[solenoid]] and a [[Soft Iron|soft iron]] core. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Electromagnets=== | ||
| + | : [[Electromagnet]]s only work when there is a [[Direct Current|direct current]] passing through the [[solenoid]] | ||
| + | : An [[electromagnet]] can be turned off and on. | ||
| + | : The strength of an [[electromagnet]] depends on; the number of coils of [[wire]] in the [[solenoid]], the [[Electrical Current|current]] through the [[solenoid]] and how easily the [[Soft Iron|soft iron]] core can be [[Magnetise|magnetised]]. | ||
| + | *The more coils of [[wire]] in the [[solenoid]] the stronger the [[electromagnet]]. | ||
| + | *The greater the [[Electrical Current|current]] through the [[solenoid]] the stronger the [[electromagnet]]. | ||
| + | *The more easily [[Magnetise|magnetised]] the [[Soft Iron|soft iron]] core, the stronger the [[electromagnet]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:MagneticFieldLinesElectromagnet.png|center|400px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
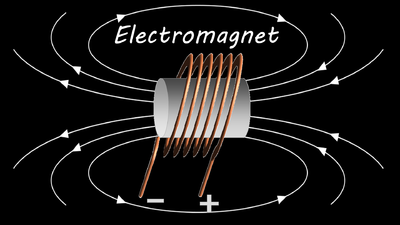
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The direction of the [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] can be changed by changing the direction of the [[Electrical Current|current]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Compared to a Bar Magnet=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |'''Advantages of an Electromagnet over a Bar Magnet''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |'''Disadvantages of an Electromagnet compared to a Bar Magnet''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| + | Changing the [[Electrical Current|current]] can change the strength of an [[electromagnet]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | An [[electromagnet]] can be turned on an off by turning the [[Electrical Current|current]] on and off. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The direction of the [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] can be changed in an [[electromagnet]] by changing the direction of the [[Electrical Current|current]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| + | [[Electromagnet]]s require a source of power to work. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Electromagnet]]s increase in [[temperature]] as they are used. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Applications=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:RelayDiagram1.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:RelayDiagram2.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
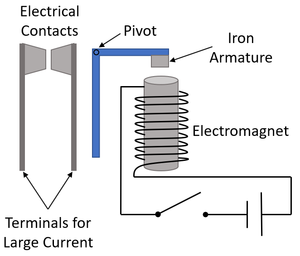
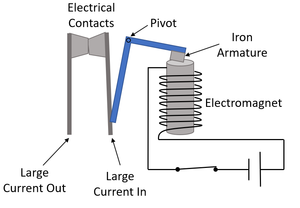
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" colspan = "2"|When the switch is closed the [[electromagnet]] pulls the [[Iron]] armature towards it. This causes the the two large electrical contacts to touch. When the [[switch]] is open the [[electromagnet]] turns off and the contacts separate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is used for safety reasons so that a [[switch]] can be used to operate a [[circuit]] with a very large [[Electrical Current|current]] indirectly. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:BellDiagram1.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:BellDiagram2.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
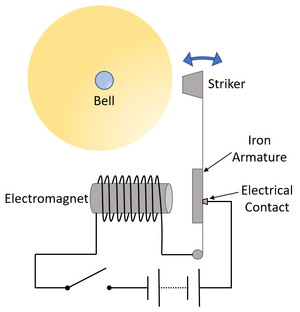
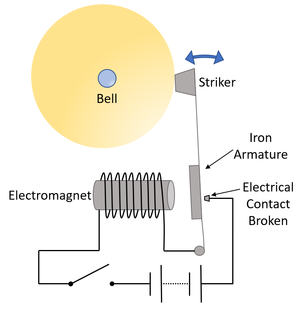
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" colspan = "2"|When the [[switch]] is closed the [[electromagnet]] pulls the [[Iron]] armature towards it. This causes the a [[metal]] arm to bend and the striker to hit the bell. When the arm bends the [[circuit]] is broken and the [[electromagnet]] turns off. This allows the striker to move back away from the bell, where electrical contact is made and the process repeats. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Electromagnets, page 219, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Electromagnets, pages 217-219, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Electromagnets, pages 225-6. GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Electromagnets, pages 279, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Electromagnets, pages 292, 293, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Electromagnets, page 171, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Electromagnets, page 198, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Electromagnets, page 405, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Electromagnets, page 88, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Electromagnets, pages 270-272, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Electromagnets; uses, pages 271-279, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Electromagnets, pages 123, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:23, 5 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
An electromagnet is a magnet made from a coil of wire wrapped around a soft iron core.
About Electromagnets
- Electromagnets only work when there is a direct current passing through the coil of wire.
- An electromagnet can be turned off and on.
- The strength of an electromagnet depends on; the number of coils of wire, the current through the wire and how easily the soft iron core can be magnetised.
- The more coils of wire the stronger the electromagnet.
- The greater the current through the wire the stronger the electromagnet.
- The more easily magnetised the soft iron core, the stronger the electromagnet.
| The direction of the magnetic field can be changed by changing the direction of the current. |
Compared to a Bar Magnet
| Advantages of an Electromagnet over a Bar Magnet | Disadvantages of an Electromagnet compared to a Bar Magnet |
|
Changing the current can change the strength of an electromagnet. An electromagnet can be turned on an off by turning the current on and off. The direction of the magnetic field can be changed in an electromagnet by changing the direction of the current. |
Electromagnets require a source of power to work. Electromagnets increase in temperature as they are used. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
An electromagnet is a magnet made from a solenoid and a soft iron core.
About Electromagnets
- Electromagnets only work when there is a direct current passing through the solenoid
- An electromagnet can be turned off and on.
- The strength of an electromagnet depends on; the number of coils of wire in the solenoid, the current through the solenoid and how easily the soft iron core can be magnetised.
- The more coils of wire in the solenoid the stronger the electromagnet.
- The greater the current through the solenoid the stronger the electromagnet.
- The more easily magnetised the soft iron core, the stronger the electromagnet.
| The direction of the magnetic field can be changed by changing the direction of the current. |
Compared to a Bar Magnet
| Advantages of an Electromagnet over a Bar Magnet | Disadvantages of an Electromagnet compared to a Bar Magnet |
|
Changing the current can change the strength of an electromagnet. An electromagnet can be turned on an off by turning the current on and off. The direction of the magnetic field can be changed in an electromagnet by changing the direction of the current. |
Electromagnets require a source of power to work. Electromagnets increase in temperature as they are used. |
Applications
| When the switch is closed the electromagnet pulls the Iron armature towards it. This causes the the two large electrical contacts to touch. When the switch is open the electromagnet turns off and the contacts separate.
This is used for safety reasons so that a switch can be used to operate a circuit with a very large current indirectly. | |
| When the switch is closed the electromagnet pulls the Iron armature towards it. This causes the a metal arm to bend and the striker to hit the bell. When the arm bends the circuit is broken and the electromagnet turns off. This allows the striker to move back away from the bell, where electrical contact is made and the process repeats. | |
References
AQA
- Electromagnets, page 219, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Electromagnets, pages 217-219, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Electromagnets, pages 225-6. GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Electromagnets, pages 279, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Electromagnets, pages 292, 293, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Electromagnets, page 171, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Electromagnets, page 198, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Electromagnets, page 405, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Electromagnets, page 88, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Electromagnets, pages 270-272, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Electromagnets; uses, pages 271-279, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel