Difference between revisions of "Pure"
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Pure]] [[Gold]] is a [[solid]] made of only [[Gold]] [[atom]]s. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Pure]] [[Gold]] is a [[solid]] made of only [[Gold]] [[atom]]s. | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Pure]] [[Mercury]] is a [[Liquid]] made of only [[Mercury]] [[atom]]s. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Pure]] [[Mercury (Element)|Mercury]] is a [[Liquid]] made of only [[Mercury (Element)|Mercury]] [[atom]]s. |
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Pure]] [[Oxygen]] is a [[gas]] made of only [[Oxygen]] [[atom]]s. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Pure]] [[Oxygen]] is a [[gas]] made of only [[Oxygen]] [[atom]]s. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
===About Purity=== | ===About Purity=== | ||
: [[Pure]] does NOT mean good, healthy or natural. | : [[Pure]] does NOT mean good, healthy or natural. | ||
| + | : '''Purity''' is important for ensuring that when [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]]s take place there are no unwanted [[product]]s caused by the '''impurities'''. | ||
| + | : '''Impurities''' can change the [[property|properties]] of a [[substance]] such as its [[Melting Point|melting point]], [[Electrical Conductivity|electrical conductivity]] or [[Strength (Property)|strength]]. This means '''purity''' is essential when using [[substance]]s for certain [[application]]s where those [[property|properties]] important. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
'''Purity''' may refer to: | '''Purity''' may refer to: | ||
*A '''pure''' [[element]] - A [[substance]] containing only one type of [[atom]]. | *A '''pure''' [[element]] - A [[substance]] containing only one type of [[atom]]. | ||
*A '''pure''' [[compound]] - A [[substance]] containing only one [[chemical]] [[compound]]. | *A '''pure''' [[compound]] - A [[substance]] containing only one [[chemical]] [[compound]]. | ||
| − | : ''' | + | ===Detecting Purity=== |
| − | + | : The '''purity''' of a sample can be determined by: | |
| + | *Looking at its [[property|properties]] such as the [[Melting Point|melting point]] and [[Boiling Point|boiling point]]. If these are spread over a range of [[temperature]]s or different from the known values for the [[pure]] [[substance]] then the sample is not [[pure]]. For example to test if a sample of [[Water]] is [[pure]] it can be [[melting|melted]] from [[Ice]] and [[boiling|boiled]] from [[liquid]] [[Water]]. If the [[Melting Point|melting point]] is exactly 0°C and the [[Boiling Point|boiling point]] is exactly 100°C, then the [[Water]] is [[pure]]. | ||
| + | *Using [[Chromatography]] to observe if a [[soluble]] [[solid]] is a [[mixture]] which [[Separating Mixtures|separate]]s on piece of [[Chromatography]] paper (there is more than one dot on the [[Chromatogram]]). For example a sample of coloured ink can be placed on some [[chromatography]] paper. Using a suitable [[solvent]] the [[solute]]s within the ink will move along the [[chromatography]] paper. If there is more than one [[solute]] then ink will split into more than one dot on the [[Chromatogram]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10211 ''Purity, page 150, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Purity, page 198, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Purity, page 252, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d217 ''Purity, page 86, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Purity, pages 180-181, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945679/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945679&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a2db42f7b4bdf10cafaafa3bb9120940 ''Impurities, page 26, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Impurities, page 98, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945679/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945679&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a2db42f7b4bdf10cafaafa3bb9120940 ''Impurities; in tap water, page 100, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359829/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359829&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=90e8d7b4f039d53035238fa0320fe00b ''Pure substances, pages 40-41, 48-49, 127, 199, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:11, 18 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A pure substance is one that contains only one type of chemical.
About Pure Substances
- The opposite of a pure substance would be a mixture of substances.
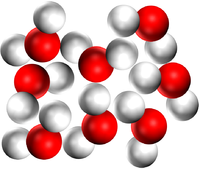
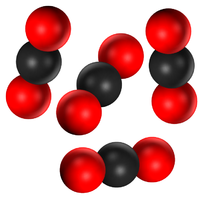
- A substance can be pure because it is made of only one element or it can be pure because it is made of only one compound.
- The word pure is often used in food adverts to mean there is only one ingredient, eg pure orange juice contains only oranges, but most people confuse it for meaning something that is healthy, natural or good. Be careful not to confuse this for the real meaning of pure.
Examples
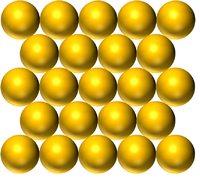
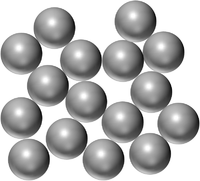
| Pure Gold is a solid made of only Gold atoms. | Pure Mercury is a Liquid made of only Mercury atoms. | Pure Oxygen is a gas made of only Oxygen atoms. |
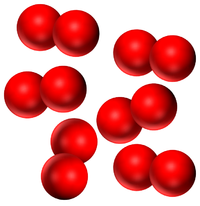
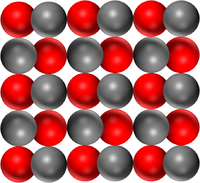
| Pure Magnesium Oxide is a solid made of only the compound Magnesium Oxide | Pure water is a liquid made of only the compound H2O. | Pure Carbon Dioxide is a gas made of only Carbon Dioxide molecules. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A pure substance is one that contains only one type of chemical.
About Purity
- Pure does NOT mean good, healthy or natural.
- Purity is important for ensuring that when reactions take place there are no unwanted products caused by the impurities.
- Impurities can change the properties of a substance such as its melting point, electrical conductivity or strength. This means purity is essential when using substances for certain applications where those properties important.
Purity may refer to:
- A pure element - A substance containing only one type of atom.
- A pure compound - A substance containing only one chemical compound.
Detecting Purity
- The purity of a sample can be determined by:
- Looking at its properties such as the melting point and boiling point. If these are spread over a range of temperatures or different from the known values for the pure substance then the sample is not pure. For example to test if a sample of Water is pure it can be melted from Ice and boiled from liquid Water. If the melting point is exactly 0°C and the boiling point is exactly 100°C, then the Water is pure.
- Using Chromatography to observe if a soluble solid is a mixture which separates on piece of Chromatography paper (there is more than one dot on the Chromatogram). For example a sample of coloured ink can be placed on some chromatography paper. Using a suitable solvent the solutes within the ink will move along the chromatography paper. If there is more than one solute then ink will split into more than one dot on the Chromatogram.
References
AQA
- Purity, page 150, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Purity, page 198, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Purity, page 252, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Purity, page 86, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Purity, pages 180-181, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
OCR
- Impurities, page 26, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Impurities, page 98, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Impurities; in tap water, page 100, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Pure substances, pages 40-41, 48-49, 127, 199, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR