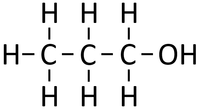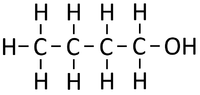Difference between revisions of "Alcohol"
(→About Alcohol Molecules) |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
===About Alcohol Molecules=== | ===About Alcohol Molecules=== | ||
| − | : [[Alcohol]]s are a [[Homologous Series|homologous series]] of [[ | + | : [[Alcohol]]s are a [[Homologous Series|homologous series]] of [[Organic Compound|organic compounds]]. |
: The [[Functional Group|functional group]] of the [[Alcohol]]s is the OH group attached to a [[Carbon]] [[atom]]. | : The [[Functional Group|functional group]] of the [[Alcohol]]s is the OH group attached to a [[Carbon]] [[atom]]. | ||
: [[Alcohol]]s are long chains of [[Carbon]] [[atom]]s [[Covalent Bond|covalently bonded]] together with [[Single Bond|single bonds]], an OH group attached to a [[Carbon]] [[atom]] and [[Hydrogen]] [[atom]]s taking the remaining [[Chemical Bond|bonds]]. | : [[Alcohol]]s are long chains of [[Carbon]] [[atom]]s [[Covalent Bond|covalently bonded]] together with [[Single Bond|single bonds]], an OH group attached to a [[Carbon]] [[atom]] and [[Hydrogen]] [[atom]]s taking the remaining [[Chemical Bond|bonds]]. | ||
Revision as of 13:42, 17 January 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Alcohol is a legal drug sold as a drink.
About Alcohol
- Alcohol has intoxicating effects on humans, causing them to behave in ways they wouldn't normally when sober.
- Alcohol is toxic in large quantities and over long periods of time.
- Alcohol poisoning can cause a person to die if too much alcohol is consumed in a short period of time. However, usually people do not die directly from the alcohol but because they drown in their own vomit or become involved in an accident.
- Prolonged alcohol abuse can lead to liver and kidney damage and even failure. This may require a liver transplant or a kidney transplant.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
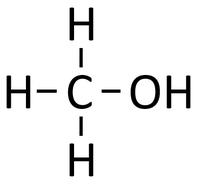
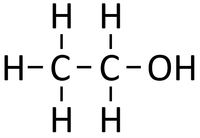
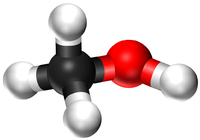
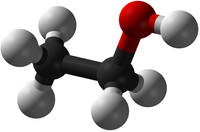
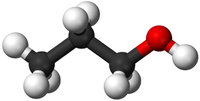
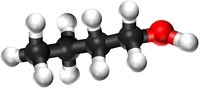
Alcohols are organic compounds containing an OH group attached to a Carbon chain and the general formula; CnH2n+1OH. The term alcohol may also be used to refer to one particular type of alcohol called ethanol which is used as a drug.
About Alcohol Molecules
- Alcohols are a homologous series of organic compounds.
- The functional group of the Alcohols is the OH group attached to a Carbon atom.
- Alcohols are long chains of Carbon atoms covalently bonded together with single bonds, an OH group attached to a Carbon atom and Hydrogen atoms taking the remaining bonds.
There are several alcohol molecules you should know:
Examples
| Methanol | Ethanol | Propanol | Butanol | |
| Chemical Formula (CnH2n+2) | CH3OH | C2H5OH | C3H7OH | C4H9OH |
| Structural Formula | CH3OH | CH3CH2OH | CH3CH2CH2OH | CH3CH2CH2CH2OH |
| Structural Diagram | ||||
| Ball and Stick Model |