Difference between revisions of "Condensation Polymerisation"
(→Forming Polyesters) |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
|[[File:StructuralDiagramPolyester.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:StructuralDiagramPolyester.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
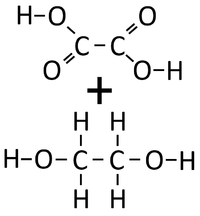
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |Ethandioate and Ethandiol can [[Chemical Reaction|react]] together in a '''Condensation Polymerisation'''. |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[Polyester]] is formed. |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:55, 19 January 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4 Higher
Meaning
Condensation polymerisation is a reaction in which monomers combine to form polymers producing a H2O or HCl molecule for each addition of a monomer.
About Condensation Polymerisation
- Condensation polymerisation reactions are called condensation reactions because they usually produce Water, but they may also produce other small molecules such as HCl.
- Condensation polymerisation reactions happen commonly in biological organisms.
Forming Polyesters
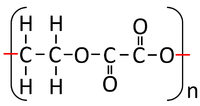
- Condensation polymerisation reactions which produce Water can happen when one end of a molecule carries an -OH group while the other end carries a -COOH group. These react together joining the molecules forming a Polyester.
- Condensation polymerisation reactions which produce Water can also happen when one molecule carries two -OH groups at either end of the molecule while the other molecule carries two -COOH groups. These two molecules react together joining the molecules forming a Polyester and producing Water.
| Ethandioate and Ethandiol can react together in a Condensation Polymerisation. | A Polyester is formed. |
Forming Polysaccharides
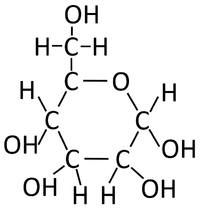
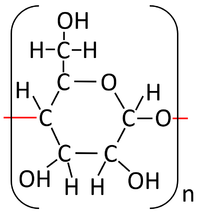
- The condensation polymerisation reaction of monosaccharides produces a polysaccharide and Water.
- The monosaccharide glucose can bond in a condensation polymersiation reaction to produce starch or glycogen.
n x Monosaccharides → Polysaccharide + Water
n x Glucose → Starch + Water
Where 'n' represents an integer.
| Text | Text | Text |
Forming Proteins
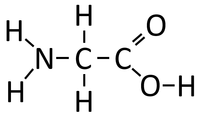
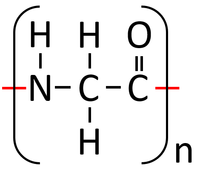
- Condensation polymerisation reactions of Peptides (Amino Acids) produce Polypeptides (Protiens) and Water.
- Each Amino Acid has an NH2 group which acts as a base and an -COOH group which acts as an acid. These functional groups react to produce Polypeptides and Water.
n x Peptides → Polypeptide + Water
<chem>nH2NCH2COOH -> (-HNCH2CO-) + nH2O</chem>
Where 'n' represents an integer.
| Text | Text | Text |