Difference between revisions of "Sugar"
(→Testing For Sugars) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===About Sugar=== | ===About Sugar=== | ||
====Sugar Molecules==== | ====Sugar Molecules==== | ||
| − | : Sugar | + | : '''Sugar''' [[molecule]]s are referred to as 'simple [[molecule]]s' which can be quickly [[Absorb (Biology)|absorbed]] into the body to provide [[energy]] by [[respiration]]. |
: You should know: | : You should know: | ||
*Glucose - A sugar found in syrup and sweets. | *Glucose - A sugar found in syrup and sweets. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
====Testing For Sugars==== | ====Testing For Sugars==== | ||
: [[Glucose]] and Fructose can be detected with the [[Benedict's Test]]. | : [[Glucose]] and Fructose can be detected with the [[Benedict's Test]]. | ||
| − | : Sucrose cannot be detected with the [[Benedict's Test]] unless you first react it with dilute | + | : [[Sucrose]] cannot be detected with the [[Benedict's Test]] unless you first react it with [[dilute]] [[Hydrochloric Acid]]. |
=====Method===== | =====Method===== | ||
| − | : 1. A sample of food is | + | : 1. A sample of food is [[dissolve]]d in [[water]]. |
| − | : 2. The solution is added to blue Benedict's solution in a boiling tube. | + | : 2. The solution is added to blue [[Benedict's Test|Benedict's]] [[solution]] in a [[Boiling Tube|boiling tube]]. |
| − | : 3. The solution is kept at 90°C for up to 10 minutes. | + | : 3. The [[solution]] is kept at 90°C for up to 10 minutes. |
| − | : 4. A colour change indicates the presence of glucose or fructose. If they are present the solution will eventually turn brick red or brown. | + | : 4. A colour change indicates the presence of [[glucose]] or [[fructose]]. If they are present the solution will eventually turn brick red or brown. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
If this was done with sucrose the Benedict's solution would stay blue. | If this was done with sucrose the Benedict's solution would stay blue. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | '''Sugar''' is a term used to refer to several [[monosaccharide]]s and [[disaccharide]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Sugar=== | ||
| + | : '''Sugar''' [[molecule]]s can join together in [[Condensation Polymerisation|condensation polymerisation]] [[Chemical Reaction|reactions]] to form [[polysaccharide]]s. | ||
Revision as of 15:43, 19 January 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Sugar is a simple carbohydrate found in food and is a source of energy for respiration.
About Sugar
Sugar Molecules
- Sugar molecules are referred to as 'simple molecules' which can be quickly absorbed into the body to provide energy by respiration.
- You should know:
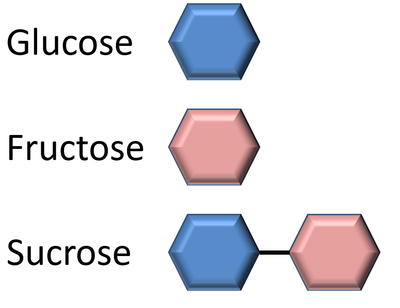
- Glucose - A sugar found in syrup and sweets.
- Fructose - A sugar found in fruits.
- Sucrose - Found in white sugar which is made of one glucose molecule and one fructose molecule bonded together.
| There are many different sugar molecules. These are just three examples. |
Sugar in foods
| Fruit has lots of sugar but is healthy because it also has vitamins and fibre inside. | Yoghurt has a lot of sugar but there are also some health parts like a mineral called Calcium. | Sweets are full of sugar with nothing healthy in them. | Energy drinks have nothing healthy in them and are packed with sugar. |
Testing For Sugars
- Glucose and Fructose can be detected with the Benedict's Test.
- Sucrose cannot be detected with the Benedict's Test unless you first react it with dilute Hydrochloric Acid.
Method
- 1. A sample of food is dissolved in water.
- 2. The solution is added to blue Benedict's solution in a boiling tube.
- 3. The solution is kept at 90°C for up to 10 minutes.
- 4. A colour change indicates the presence of glucose or fructose. If they are present the solution will eventually turn brick red or brown.
| When sugar is present the Benedict's solution turns from blue through several colours until it becomes brick red or brown.
If this was done with sucrose the Benedict's solution would stay blue. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Sugar is a term used to refer to several monosaccharides and disaccharides.
About Sugar
- Sugar molecules can join together in condensation polymerisation reactions to form polysaccharides.