Difference between revisions of "Fractional Distillation"
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
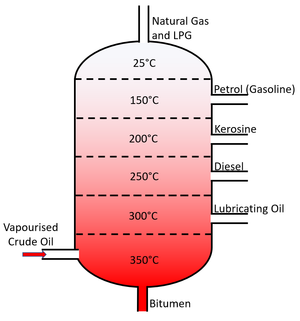
: '''Fractional Distillation''' relies on the different [[Boiling Point|boiling points]] of [[liquid]]s. By [[heating]] all [[liquid]]s beyond their [[Boiling Point]] they can be turned into a [[gas]]. Each [[gas]] can then be cooled and [[condensing|condensed]] in tubes kept just below the [[Boiling Point|boiling point]] of each fraction. | : '''Fractional Distillation''' relies on the different [[Boiling Point|boiling points]] of [[liquid]]s. By [[heating]] all [[liquid]]s beyond their [[Boiling Point]] they can be turned into a [[gas]]. Each [[gas]] can then be cooled and [[condensing|condensed]] in tubes kept just below the [[Boiling Point|boiling point]] of each fraction. | ||
| + | : [[Crude Oil]] is [[Separating Mixtures|separated]] using '''fractional distillation'''. | ||
Revision as of 20:11, 24 January 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Fractional distillation is a technique which can be used to separate two or more solvents from solution.
About Fractional Distillation
Fractional Distillation is only be used for:
- Separating a solution to recover multiple solvents.
Fractional Distillation cannot be used for:
- Separating two solutes from each other in solution - Chromatography
- Separating an insoluble solid from a soluble solid - Filtration
- Fractional Distillation relies on the different boiling points of liquids. By heating all liquids beyond their Boiling Point they can be turned into a gas. Each gas can then be cooled and condensed in tubes kept just below the boiling point of each fraction.
- Crude Oil is separated using fractional distillation.