Difference between revisions of "Covalent Bond"
(→About Covalent Bonds) |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
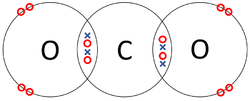
| style="height:20px; width:250px; text-align:center;" |Each [[Oxygen]] shares two of its [[electron]]s with the [[Carbon]] [[atom]] while the [[Carbon]] [[atom]] shares two [[electron]]s with each [[Oxygen]] [[atom]]. | | style="height:20px; width:250px; text-align:center;" |Each [[Oxygen]] shares two of its [[electron]]s with the [[Carbon]] [[atom]] while the [[Carbon]] [[atom]] shares two [[electron]]s with each [[Oxygen]] [[atom]]. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158762/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158762&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a0fffa35b3ea49a63404f6704e0df7cc ''Covalent bond, pages 57-9, 62-3, 72-5, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09812 ''Covalent bonds, page 116, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d95 ''Covalent bonds, page 31, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Covalent bonds, pages 154, 156-7, 163, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Covalent bonds, pages 29, 78-88, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Covalent bonds, pages 29, 80-90, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Covalent bonds, pages 38, 44-51, 149, 224-225, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Covalent bonds, pages 41-2, 47-8, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Covalent bonds; giant covalent substances, page 44, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Covalent bonds; giant covalent substances, pages 159-60, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 23:06, 3 November 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond in which atoms share electrons with one another.
About Covalent Bonds
- Atoms are more chemically stable when their outer shell is full of electrons. One way atoms can have a full outer shell is by sharing some electrons with other atoms, this is a covalent bond.
- Covalent bonds happen between non-metal elements.
- Covalent bonds can be represented by a Dot and Cross Diagram to show how the electrons are shared between the outer shells of different atoms.
Examples
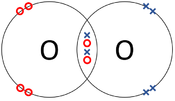
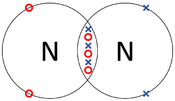
| The two Oxygen atoms each share two of their electrons with one another. | The two Nitrogen atoms each share three of their electrons with one another. | Each Oxygen shares two of its electrons with the Carbon atom while the Carbon atom shares two electrons with each Oxygen atom. |
References
AQA
- Covalent bond, pages 57-9, 62-3, 72-5, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Covalent bonds, page 116, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Covalent bonds, page 31, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Covalent bonds, pages 154, 156-7, 163, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Covalent bonds, pages 29, 78-88, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Covalent bonds, pages 29, 80-90, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Covalent bonds, pages 38, 44-51, 149, 224-225, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Covalent bonds, pages 41-2, 47-8, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Covalent bonds; giant covalent substances, page 44, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Covalent bonds; giant covalent substances, pages 159-60, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA