Difference between revisions of "Protein"
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Polypeptides, page 173, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Polypeptides, page 173, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Polypeptides, pages 192-3, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Polypeptides, pages 192-3, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158754/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158754&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=27ad53b0283feeff7fc5ae04a9e205f459 ''Protein, pages 101, 104, 108, 192, 238, 241, 246-7, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158762/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158762&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a0fffa35b3ea49a63404f6704e0df7cc ''Protein, pages 226-7, 251, 253, 283, 322, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Protein, test for, page 48, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10204 ''Proteins (test for), page 28, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Proteins, page 173, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Proteins, page 193, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Proteins, page 246, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d215 ''Proteins, page 84, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Proteins, page 85, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Proteins, pages 34, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359373/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359373&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=952a73bbb09d222ecc4b50d200679849 ''Proteins, pages 41, 46, 48, 129, 141, 204-205, 207, 309, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Proteins; function of, page 85, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Proteins; test for, page 32, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 22:53, 10 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Proteins are molecules in our diet that are used by our bodies for growth and repair.
About Proteins
- There are many different proteins.
- Protein is used to build muscles and repair injuries.
- Not enough protein can cause a disease called Kwashiorkor.
Sources of Protein
| Meat provides lots of protein for a balanced diet. | You can help keep your diet balanced by eating lots of different beans. | Nuts are the seeds of trees and are part of a balanced diet. | There are many different kinds of peas that can help make sure you have a balanced diet. |
Testing For Protein
Method
- 1. Take a small sample of food and dissolve it in water.
- 2. Add some Biuret to the solution.
- 3. If it turns from blue to purple then the food contained protein.
| This Biuret has turned purple, indicating protein is present. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Proteins, also known as polypeptides, are large polymer molecules made from amino acids that are used by our bodies for growth and repair.
About Proteins
- Proteins (polypeptides) are formed in polymerisation reactions of Amino Acids (peptides).
- Proteins are broken down by our digestive systems into amino acids which are then transported around the body by our blood.
- Cells build new proteins from amino acids in a process called protein synthesis which takes place at the ribosomes in cells.
- Protein is essential to build enzymes which control the metabolic processes inside the cell.
- A single protein can be made of millions of amino acids bonded together.
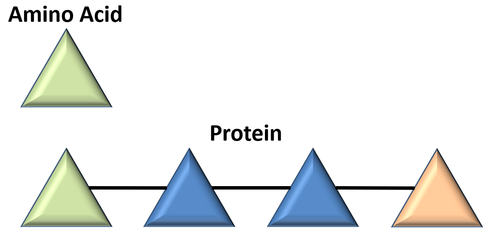
| This diagram represents an amino acid and a small protein made of 3 different amino acids. |
Sources of Protein
| Meat provides lots of protein for a balanced diet. | You can help keep your diet balanced by eating lots of different beans. | Nuts are the seeds of trees and are part of a balanced diet. | There are many different kinds of peas that can help make sure you have a balanced diet. |
Testing For Protein
Method
- 1. Take a small sample of food and dissolve it in water.
- 2. Add some Biuret to the solution.
- 3. If it turns from blue to purple then the food contained protein.
| This Biuret has turned purple, indicating protein is present. |
References
AQA
- Polypeptide, page 251, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polypeptides, page 173, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Polypeptides, pages 192-3, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
References
AQA
- Protein, pages 101, 104, 108, 192, 238, 241, 246-7, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Protein, pages 226-7, 251, 253, 283, 322, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Protein, test for, page 48, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Proteins (test for), page 28, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Proteins, page 173, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Proteins, page 193, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Proteins, page 246, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Proteins, page 84, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Proteins, page 85, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Proteins, pages 34, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Proteins, pages 41, 46, 48, 129, 141, 204-205, 207, 309, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Proteins; function of, page 85, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Proteins; test for, page 32, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA