Difference between revisions of "Light Emitting Diode"
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
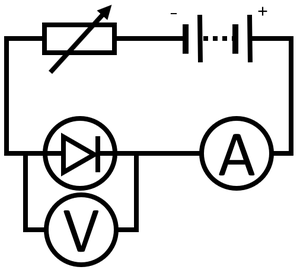
#Reverse the connections on the [[battery]] and repeat steps 4 and 5 to find the I-V relationship for negative [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] and [[Electrical Current|current]]. | #Reverse the connections on the [[battery]] and repeat steps 4 and 5 to find the I-V relationship for negative [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] and [[Electrical Current|current]]. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''LED (light emitting diode), page 52, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 02:04, 8 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
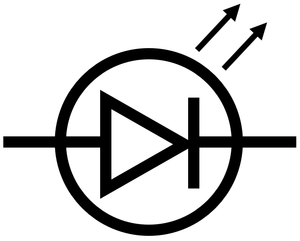
A light emitting diode (LED) is an electrical component which emits light when electricity passes through in one direction and prevents electricity from going in the reverse direction.
About Light Emitting Diodes
- LEDs have a low resistance in one direction and emit light but a very high resistance in the reverse direction and do not emit light.
- LEDs can be used to change an alternating current into a direct current.
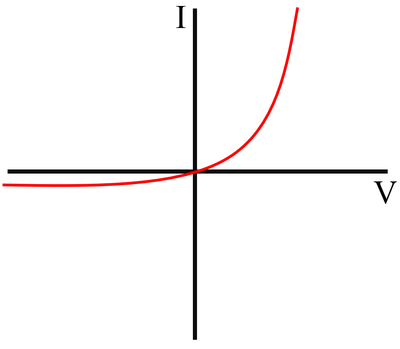
IV Graph
Description
The IV Graph for an LED shows that:
- For a positive potential difference the current increases rapidly with an increase in potential difference
- For a negative potential difference the current remains negligible and does not increase as the potential difference becomes larger.
Explanation
- The resistance of an LED is very low for current in the forward direction and very high in the back direction.
Obtaining the IV Graph
|