Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A catalyst is a chemical which can increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the reaction.
About Catalysts
- A catalyst is neither are reactant nor a product in a reaction but it can make the reaction happen more quickly.
Examples
- Chlorophyll is a catalyst for the reaction that allows plants to turn Carbon Dioxide and Water into Glucose and Oxygen during photosynthesis.
- Manganese Dioxide is a catalyst that speeds up the break down of Hydrogen Peroxide into Water and Oxygen.
- Enzymes are a type of biological catalyst that can speed up reaction inside an organism.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
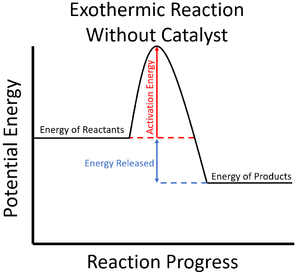
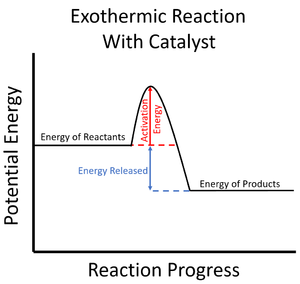
A catalyst is a chemical which can increase the rate of reaction and lower the activation energy for a particular reaction.
About Catalysts
- Catalysts provide a different reaction pathway for the reactants to form the products.
- Catalysts can lower the activation energy needed to start a Chemical Reaction.
| The activation energy is shown to be high in this reaction profile for an exothermic reaction without a catalyst. | The activation energy is shown to be low in this reaction profile for an exothermic reaction with a catalyst. |
- Since the particles in the reaction mixture will all have different amounts of energy (see Kinetic Theory), not all of them will have enough energy to react when they collide (see Collision Theory). Adding a catalyst lowers this activation energy so more particles have enough energy to react, increasing the rate of reaction.