Rate of Reaction
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Rate of reaction is a measure of how quickly the reactants react to create the products.
About the Rate of Reaction
- The longer the time taken for a reaction the lower the rate of reaction. The shorter the time taken for a reaction the higher the rate of reaction.
- High rates of reaction are important to in industries where a lot of products are needed in a short amount of time. This can save money.
- Low rates of reaction are important in materials that corrode with chemicals in the environment. This allows them to last a long time before destroyed by Oxidation or chemical weathering.
Examples
| Rusting has a low rate of reaction. | Burning Magnesium ribbon has a high rate of reaction. |
Factors Affecting the Rate of Reaction
There are several factors which affect the rate of reaction. These include:
- Temperature - The higher the temperature the faster the Chemical Reaction. Exothermic reactions may speed up as the reaction mixture becomes hotter.
- Concentration - The higher the concentration of reactants the faster the Chemical Reaction. As reactants are used they become less concentrated and the reactions tend to slow down as it progresses.
- Pressure - The higher the pressure of gaseous reactants the faster the Chemical Reaction, except in the case of some reversible reactions (see Dynamic Equilibrium).
- Surface Area - The larger the surface area of a solid reactant the faster the Chemical Reaction as there is a greater area over which the different reactants can interact.
- Catalysts - Catalysts can increase the rate of reaction by providing different reaction pathways.
The effects of temperature, concentration, pressure and surface area on rates of reaction can be explained by 'Collision Theory'.
Determining the Rate of Reaction
There are two approaches to finding the rate of reaction for some chemicals.
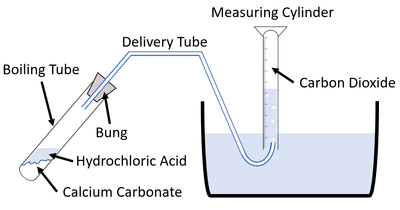
Continuously Measuring Volume of Gas
For reactions which give off a gas the volume of gas produced can be measured throughout an experiment to find the rate of reaction.
| This diagram shows a possible setup for measuring the gas given off during an experiment. |
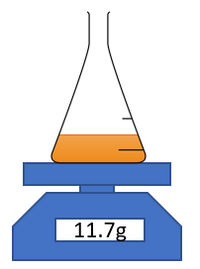
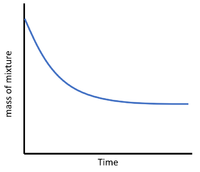
Continuously Measuring the Mass
For reactions which give off a gas the mass of reaction mixture can be measured throughout an experiment to find the rate of reaction.
| This diagram shows a possible setup for measuring the mass of the reaction mixture during an experiment. |
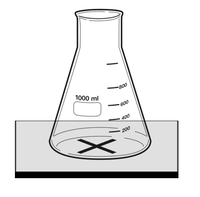
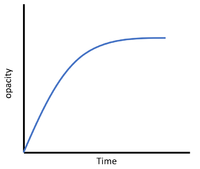
Continuously Measuring the Opacity
For reactions in which the reactants are in a transparent solution but the products form an insoluble precipitate that is opaque then the opacity can be measured.
| This diagram shows a possible setup for identifying when a mixture becomes opaque during a reaction by drawing a black cross on a white tile and observing until the cross can no longer be seen. |
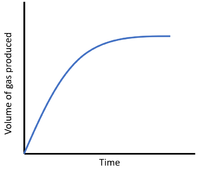
Rate of Reaction from Graphs
On a graph with time on the x-axis and the amount of reactant or product on the y-axis the rate of reaction can be seen from the gradient.
| The steep positive gradient shows a high rate of reaction as the gas is produced more quickly at the start of the reaction. | The steep negative gradient shows a high rate of reaction as the gas is being lost more quickly at the start of the reaction. | The steep negative gradient shows a high rate of reaction as the precipitate is formed more quickly at the start of the reaction. |
References
AQA
- Rate of reaction; Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide solution, pages 128, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Rate of reaction; Effects of changes in concentration, pages 127, 129, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Rate of reaction; Graphs of, pages 120, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Rate of reaction; graphs of, pages 149-50, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Rate of reaction; Influencing factors, pages 122-5, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Rate of reaction; influencing factors, pages 151-4, 156, 158, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Rate of reaction; Measurement of, pages 118-21, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Rate of reaction; measurement of, pages 147-8, 156-7, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Rates of reaction, page 164-177, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction, page 29, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction, pages 196-209, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction, pages 67- 71, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; calculating rates, page 168, 172, 173, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; calculating rates, pages 200, 204, 205, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; concentration, pages 134-135, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Rates of reaction; effect of catalyst, page 198, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; effect of catalysts, page 166, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; effect of concentration, pages 165, 176, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; effect of concentration, pages 197, 208, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; effect of surface area, page 165, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; effect of surface area, page 197, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; effect of temperature, pages 165, 166, 176, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; effect of temperature, pages 197, 198, 208, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; equilibria, pages 128-129, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Rates of reaction; experiments, pages 176, 177, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; experiments, pages 208, 209, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; graphs, pages 171- 174, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; graphs, pages 203-206, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; graphs, pages 67, 70, 71, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; measuring rates, pages 168-170, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; measuring rates, pages 200-202, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; measuring rates, pages 69, 70, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reaction; pressure, page 134, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Rates of reaction; reversible reactions, pages 138-145, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Rates of reaction; surface area, pages 130-131, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Rates of reaction; temperature, pages 132-133, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Rates of reactions, pages 128-147, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Rates of reactions, pages 26, 138-143, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reactions; catalysts, pages 136-137, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Rates of reactions; collision theory, pages 130-135, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Rates of reactions; graphs, pages 138, 142, 143, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Rates of reactions; measuring rates, pages 140, 141, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Rate of reaction in photosynthesis, page 126, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Rates of reaction, pages 10, 17, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Rates of reaction, pages 223-239, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Rates of reaction; calculating rates, pages 223, 229, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Rates of reaction; catalysts, pages 238, 239, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Rates of reaction; experiments, pages 223-225, 231-234, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Rates of reaction; graphs, pages 226-229, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Rates of reactions, pages 7, 16, 128-133, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Rates of reactions, pages 77-82, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Reaction rates, pages 136-137, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Reaction rates; factors affecting, pages 138-139, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
OCR
- Rate of reaction, pages 128-132, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Rate of reaction, pages 68-71, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Reaction rate, page 291, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Reaction rate, pages 290, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Reaction rates, pages 174-183, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Reaction rates; catalysts, pages 182-183, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Reaction rates; concentration, pages 178-179, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Reaction rates; graphs, page 304, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Reaction rates; measuring, pages 278-279, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Reaction rates; particle size, pages 180-181, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Reaction rates; pressure, pages 179, 298, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Reaction rates; temperature, pages 176-177, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR