Magnesium
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Magnesium is a Group 2 element, on the Periodic Table, with an atomic number of 12.
About Magnesium
Molecular Structure
- Magnesium has the chemical symbol Mg.
- Magnesium atoms join together in large numbers to form a giant metal molecule.
Atomic Structure
- Magnesium as 12 protons and 12 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an Atomic Number of 12 and an atomic mass of 24.
- An atom of Magnesium has only 2 electrons in its outer shell.
Properties
- Magnesium is a more reactive alkali earth metal than Beryllium but less reactive than Calcium.
- Magnesium is more reactive than Carbon on the reactivity series so it must be extracted from its ore using electrolysis.
- Magnesium reacts slowly with liquid water and strongly with steam to produce Hydrogen gas and Magnesium Hydroxide and strongly with acid to produce a Magnesium salts.
- Magnesium burns at a very high temperature with a bright white flame.
- Magnesium is a solid at room temperature.
Key Stage 4
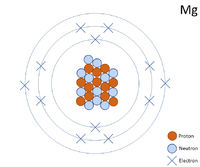
A 2 dimensional representation of the Bohr Model of a Magnesium-24 isotope with 12 protons and 12 neutrons in the nucleus and 2 electrons in the first shell, 8 in the second and 2 in the outer shell.
Meaning
Magnesium is a Group 2 element, on the Periodic Table, with 12 protons in the nucleus.
About Magnesium
Molecular Structure
- Magnesium has the chemical formula Mg.
- Magnesium atoms join together in a giant metallic structure.
Atomic Structure
- The most stable isotope of Magnesium has 12 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an atomic mass of 24.
- An atom of Magnesium has only 2 electrons in its outer shell.
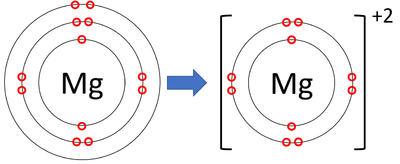
- Magnesium ions have lost two electrons to become positively charged.
| A diagram showing the formation of a Magnesium ion. |
Properties
- Magnesium is a more reactive alkali earth metal than Beryllium but less reactive than Calcium.: Magnesium is more reactive than Carbon on the reactivity series so it must be extracted from its ore using electrolysis.
- Magnesium reacts slowly with liquid water and strongly with steam to produce Hydrogen gas and Magnesium Hydroxide and strongly with acid to produce a Magnesium salts.
- Magnesium burns at a very high temperature with a bright white flame.
- Magnesium is a solid at standard temperature and pressure.