Difference between revisions of "Feynman Diagram"
(→Constructing a Feynman Diagram) |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
===Constructing a Feynman Diagram=== | ===Constructing a Feynman Diagram=== | ||
| − | : '''Feynman Diagrams''' can be constructed from the equations representing a [[Subatomic Particle|particle]] [[Fundamental | + | : '''Feynman Diagrams''' can be constructed from the equations representing a [[Subatomic Particle|particle]] [[Fundamental Interactions|interaction]]. |
: The [[Subatomic Particle|particles]] at the start of the [[Nuclear Equation|equation]] are written at the bottom of the '''Feynman diagram''' while the [[product]]s are written at the top. | : The [[Subatomic Particle|particles]] at the start of the [[Nuclear Equation|equation]] are written at the bottom of the '''Feynman diagram''' while the [[product]]s are written at the top. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
|[[File:FeynmanDiagramElectronCapture.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:FeynmanDiagramElectronCapture.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Subatomic Particle|particles]] prior to the [[Fundamental | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Subatomic Particle|particles]] prior to the [[Fundamental Interactions|interaction]] are drawn first at the bottom of the '''Feynman diagram'''. |
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Subatomic Particle|particles]] after the [[Fundamental | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Subatomic Particle|particles]] after the [[Fundamental Interactions|interaction]] are drawn at the top of the '''Feynman diagram'''. It should be recognised that [[Conservation of Baryon Number|baryon conservation]] means a [[baryon]] becomes another [[baryon]] and [[Conservation of Lepton Number|lepton conservation]] means that a [[lepton]] is transformed from one type of [[lepton]] into another. |
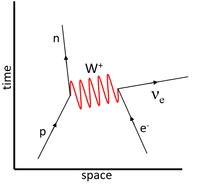
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |Finally the [[boson]] mediating the [[Fundamental | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |Finally the [[boson]] mediating the [[Fundamental Interactions|interaction]] is added as a [[wave]] between the two points of [[Fundamental Interactions|interaction]]. In this case a [[proton]] loses its [[Positive Charge|positive charge]] therefore it is carried away to the [[electron]] via the [[W-boson|W<sup>+</sup> boson]] transforming the [[electron]] into an [[Electron Neutrino|electron neutrino]]. |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 18:56, 31 July 2019
Contents
Key Stage 5
Meaning
A Feynman diagram is a type of graph used to represent the interactions between subatomic particles.
About Feynman Diagrams
- Feynman diagrams have time on the y-axis and space on the z-axis.
- Feynman diagrams are used to simplify complex equations used to represent subatomic particle interactions.
- Particles with a high velocity are seen as having shallow gradients on a Feynman diagram since they travel a large distance in space over a short duration of time.
Constructing a Feynman Diagram
- Feynman Diagrams can be constructed from the equations representing a particle interaction.
- The particles at the start of the equation are written at the bottom of the Feynman diagram while the products are written at the top.
|
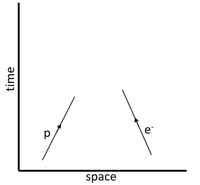
\(p + e^-\) |
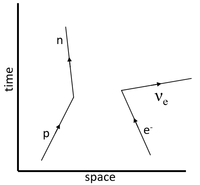
\(p + e^- \rightarrow n + \beta^- + \bar\nu_e\) |
\(p + e^- \rightarrow n + \beta^- + \bar\nu_e\) |
| The particles prior to the interaction are drawn first at the bottom of the Feynman diagram. | The particles after the interaction are drawn at the top of the Feynman diagram. It should be recognised that baryon conservation means a baryon becomes another baryon and lepton conservation means that a lepton is transformed from one type of lepton into another. | Finally the boson mediating the interaction is added as a wave between the two points of interaction. In this case a proton loses its positive charge therefore it is carried away to the electron via the W+ boson transforming the electron into an electron neutrino. |
Examples
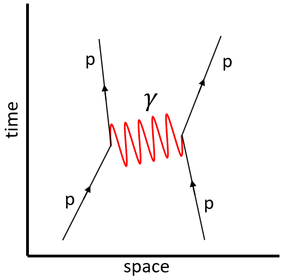
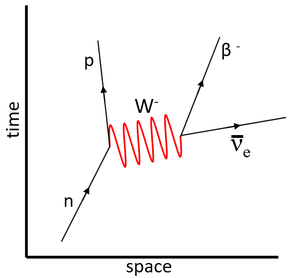
| This Feynman diagram shows the electromagnetic interaction between two protons via the virtual photon. | This Feynman diagram shows the weak interaction in which a neutron decays into a proton.
\(n \rightarrow p + \beta^- + \bar\nu_e\) |
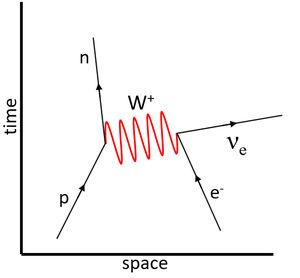
| This Feynman diagram shows the weak interaction in which a proton captures an electron to become a neutron.
\(p + e^- \rightarrow n + \nu_e\) |
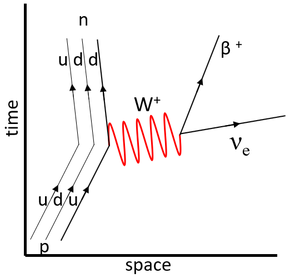
This Feynman diagram shows the weak interaction in which an up-quark decays into a down-quark, which is observed as a proton decaying into a neutron via beta emission.
\(u \rightarrow d + \beta^+ + \nu_e\) |