Nuclear Fission Reactor
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A Nuclear fission reactor is a device used to transfer energy from the nuclear potential energy store to the thermal energy store of an object with a nuclear fission reaction.
About Nuclear Fission Reactors
- In a nuclear reactor on average 1 neutron from each fission event goes on to cause one more fission event. This results in a constant release of energy.
- During nuclear fission the neutrons produced usually have too much energy to be captured by the nucleus of another atom, so they must be slowed down by a moderator to a lower energy in order for a chain reaction to occur.
- Neutrons with the right amount of energy to be captured are called thermal neutrons because they have a similar energy to molecules in the air at room temperature.
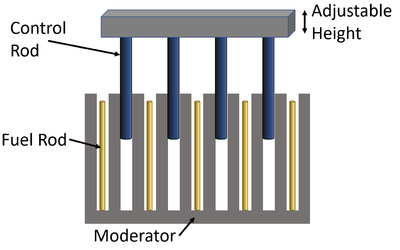
| Fuel Rods - In nuclear fission reactors unstable isotopes are in fuel rods
Moderator - The fuel rods are surrounded by a moderator which slows down the neutrons released in nuclear fission events so they can be be captured by a second nucleus to cause a second nuclear fission event. Control Rods - Large rods of Boron can be moved in and out of the reactor to slow down or stop the nuclear fission reaction by absorbing the neutrons and preventing them from moving from one fuel rod to the other. |
- The fuel rods in a nuclear reactor are slim to allow neutrons to escape the fuel rods easily. This prevents a single fuel rod from sustaining a chain reaction. The fuel rods are placed next to each other so that the neutrons released by one fuel rod are absorbed by another fuel rod. This also allows them to have control rods placed between them to stop the reaction.