Difference between revisions of "Titration"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
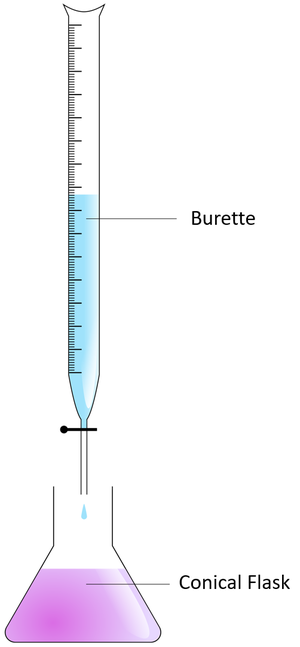
[[File:Titration.png|right|300px|thumb|A [[diagram]] showing the setup for a [[titration]].]] | [[File:Titration.png|right|300px|thumb|A [[diagram]] showing the setup for a [[titration]].]] | ||
| − | [[Titration]] is an | + | [[Titration]] is an experimental technique used to [[measure]] the exact [[Volume (Space)|volume]]s of [[acid]] and [[alkali]] needed to have a complete [[Neutralisation]] [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]]. |
===About Titration=== | ===About Titration=== | ||
Revision as of 10:26, 8 April 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Titration is an experimental technique used to measure the exact volumes of acid and alkali needed to have a complete Neutralisation reaction.
About Titration
- During a titration one of the solutions is a fixed volume and the other is is added as needed and measured as precisely and accurately as possible.
- To obtain a fixed volume a Volumetric Pipette is used.
- To measure the volume being added a Burette is used.
Method
For a fixed volume of alkali and a measured volume of acid.
- Wash the volumetric pipette and burette with distilled water then wash the volumetric pipette with the alkali and the burette with the acid to avoid contamination from previous experiments.
- Measure and record a fixed volume of alkali using the volumetric pipette.
- Add the alkali to a conical flask and then add a few drops of pH Indicator.
- Fill the burette with acid.
- Add the acid to the alkali one drip at a time, swirling the conical flask constantly to mix the reactants thoroughly.
- Repeat until the pH Indicator shows the solution is neutral.
- Record the volume of acid added to the conical flask.
- Repeat the experiment at least 3 times to produce an average.