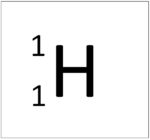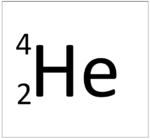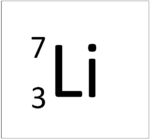Difference between revisions of "Neutron"
(→Meaning) |
(→About Neutrons) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Hydrogen''' |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Helium''' |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Lithium''' |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Beryllium''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[File:HydrogenSymbol.png|center| | + | |[[File:HydrogenSymbol.png|center|150px]] |
| − | |[[File:HeliumSymbol.png|center| | + | |[[File:HeliumSymbol.png|center|150px]] |
| − | |[[File:LithiumSymbol.png|center| | + | |[[File:LithiumSymbol.png|center|150px]] |
| − | |[[File:BerylliumSymbol.png|center| | + | |[[File:BerylliumSymbol.png|center|150px]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:left;" |This [[atom]] has an [[Atomic Number]] (Z) of 1 and a [[Relative Atomic Mass]] (A) of 1. |
Number of [[neutron]]s = A - Z | Number of [[neutron]]s = A - Z | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
Number of [[neutron]]s = 0 | Number of [[neutron]]s = 0 | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:left;" |This [[atom]] has an [[Atomic Number]] (Z) of 2 and a [[Relative Atomic Mass]] (A) of 4. |
Number of [[neutron]]s = A - Z | Number of [[neutron]]s = A - Z | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
Number of [[neutron]]s = 2 | Number of [[neutron]]s = 2 | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:left;" |This [[atom]] has an [[Atomic Number]] (Z) of 3 and a [[Relative Atomic Mass]] (A) of 7. |
Number of [[neutron]]s = A - Z | Number of [[neutron]]s = A - Z | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
Number of [[neutron]]s = 4 | Number of [[neutron]]s = 4 | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:left;" |This [[atom]] has an [[Atomic Number]] (Z) of 4 and a [[Relative Atomic Mass]] (A) of 9. |
Number of [[neutron]]s = A - Z | Number of [[neutron]]s = A - Z | ||
Revision as of 17:37, 18 July 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The Neutron is a neutral particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
About Neutrons
- Neutrons are a type of nucleon.
- Neutrons have a relative atomic charge of 0 and a relative atomic mass of 1.
- The number of neutrons in an atom can be found subtracting the Atomic Number from the Relative Atomic Mass.
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
| This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 1 and a Relative Atomic Mass (A) of 1.
Number of neutrons = A - Z Number of neutrons = 1 - 1 Number of neutrons = 0 |
This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 2 and a Relative Atomic Mass (A) of 4.
Number of neutrons = A - Z Number of neutrons = 4 - 2 Number of neutrons = 2 |
This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 3 and a Relative Atomic Mass (A) of 7.
Number of neutrons = A - Z Number of neutrons = 7 - 3 Number of neutrons = 4 |
This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 4 and a Relative Atomic Mass (A) of 9.
Number of neutrons = A - Z Number of neutrons = 9 - 4 Number of neutrons = 5 |
Key Stage 5
Meaning
A neutron (n) is a baryon made from 1 up-quark and 2 down-quarks.
About Neutrons
- A neutron is one of two baryons found in the atomic nucleus.
- Neutrons have a charge of zero and a mass of 1.67x10-27kg.
- A neutron is only stable in the nucleus of an atom. However a free neutron has a mean lifeftime of around 15 minutes before it decays via the weak interaction into a proton and an electron.
| Subatomic Particle | Quark-composition | Charge/e | Strangeness | Baryon Number | Lepton Number |
| \(udd\) | \(q=0\) | \(S=0\) | \(b=+1\) | \(l=0\) | |
| \(\bar{u}\bar{d}\bar{d}\) | \(q=0\) | \(S=0\) | \(b=-1\) | \(l=0\) |