Difference between revisions of "Metallic Bond"
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10072 ''Metallic bonds, page 120, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10072 ''Metallic bonds, page 120, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d181 ''Metallic bonds, pages 23, 35, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d181 ''Metallic bonds, pages 23, 35, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Metallic bonding, page 88, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Metallic bonding, pages 25, 63, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Metallic bonding, pages 65, 66, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
Revision as of 17:50, 22 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A metallic bond is type of chemical bond in which metal atoms are held together as a group of positive ions surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons.
About Metallic Bonds
- Metallic bonds happen between metal atoms. This can be between atoms of the same element or different metal elements (an alloy).
- In metallic bonds the atoms form a lattice of positive ions surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons.
- When metal atoms form metallic bonds they produce giant metallic structures but not simple compounds.
- More than one metal element in a metal is referred to as an alloy, not a compound.
Examples
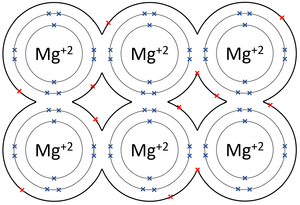
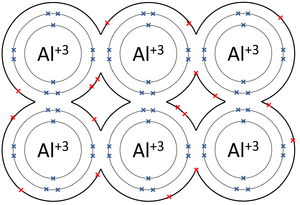
| The outer shells of the Magnesium atoms overlap allowing the two electrons in each outer shell to move freely between atoms. | The outer shells of the Aluminium atoms overlap allowing the three electrons in each outer shell to move freely between atoms. |
References
AQA
- Metallic bond, pages 57-9, 66-7, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Metallic bonding, pages 160-1, 163, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Metallic bonding, pages 52-55, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Metallic bonds, page 120, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Metallic bonds, pages 23, 35, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA