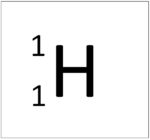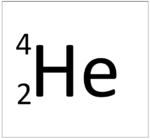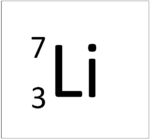Difference between revisions of "Proton"
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Protons, pages, 110, 111, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Protons, pages, 110, 111, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Protons; atomic number and mass number, page 89, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Protons; atomic number and mass number, page 89, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Protons, page 16, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Protons, page 18, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Protons, page 79, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Protons, pages 152, 155, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Protons, pages 33-37, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Protons, pages 92, 140, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
Revision as of 15:39, 27 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The Proton is a positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
About Protons
- Protons are a type of nucleon.
- Protons have a relative atomic charge of +1 and a relative atomic mass of 1.
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
| This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 1 therefore it contains 1 proton. | This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 2 therefore it contains 2 proton. | This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 3 therefore it contains 3 proton. | This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 4 therefore it contains 4 proton. |
Key Stage 5
Meaning
A proton (p) is a baryon made from 2 up-quarks and 1 down-quark.
About Protons
- The proton is denoted with a lower case p.
- A proton is one of two baryons found in the atomic nucleus.
- Protons have a charge of 1.60x10-19 Coulombs (the elementary charge) and a mass of 1.67x10-27kg.
- A proton is the most stable hadron with a half life longer than the age of the Universe.
| Subatomic Particle | Quark-composition | Charge/e | Strangeness | Baryon Number | Lepton Number |
| \(uud\) | \(Q=+1\) | \(S=0\) | \(B=+1\) | \(L=0\) | |
| \(\bar{u}\bar{u}\bar{d}\) | \(Q=-1\) | \(S=0\) | \(B=-1\) | \(L=0\) |
References
AQA
- Proton, pages 108-11, 133, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Proton, pages 13, 24-5, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Protons, page 88, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Protons, pages 117-18, 338, 339, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Protons, pages 12, 13, 19, 21, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Protons, pages 122, 123, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Protons, pages 13-15, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Protons, pages 22-25, 43, 70, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Protons, pages 22-25, 43, 72, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Protons, pages 2-3, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Protons, pages 43-45, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Protons, pages 50,95, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Protons, pages 96, 97, 104, 197, 198, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Protons, pages, 110, 111, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Protons; atomic number and mass number, page 89, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Protons, page 16, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Protons, page 18, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Protons, page 79, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Protons, pages 152, 155, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Protons, pages 33-37, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Protons, pages 92, 140, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel