Difference between revisions of "Exothermic"
| (15 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" |The [[energy]] stored in the [[reactant]]s is released in the [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reaction]] making the [[material]] increase in [[temperature]]. The [[product]]s now have less [[energy]] than the [[reactant]]s. | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" |The [[energy]] stored in the [[reactant]]s is released in the [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reaction]] making the [[material]] increase in [[temperature]]. The [[product]]s now have less [[energy]] than the [[reactant]]s. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | : [[Freezing]], [[Condensing]] and [[Depositing]] are [[exothermic]] changes because | + | : [[Freezing]], [[Condensing]] and [[Depositing]] are [[exothermic]] changes because they release [[energy]] when they happen. The [[material]] has less [[energy]] after they have happened. However, there is usually no increase in [[temperature]] because the [[material]] is usually cooled to [[State Change|change state]] because the surroundings are colder than the [[material]] during this process. |
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | An [[exothermic]] process is one that gives out [[energy]]. This usually causes surroundings to increase in [[temperature]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Exothermic Processes=== | ||
| + | ====Foundation==== | ||
| + | : [[Exothermic]] [[Chemical Reaction|reactions]] usually require [[energy]] to begin. This is called the [[Activation Energy|activation energy]]. | ||
| + | : In an [[exothermic]] process the [[Potential Energy|potential energy]] stored in the [[product]]s is less than the [[Potential Energy|potential energy]] stored in the [[reactant]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ExothermicSketchGraphKS4.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" |To start the [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] an [[Activation Energy|activation energy]] is needed. This is usually achieved by initially [[heating]] the [[reactant]]s. Once the [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] starts the [[energy]] stored in the [[reactant]]s is released in the [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reaction]] making the [[material]] increase in [[temperature]]. The [[product]]s now have less [[energy]] than the [[reactant]]s. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Higher==== | ||
| + | : In a [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reaction]] [[energy]] is needed to break the [[Chemical Bond|chemical bonds]] holding the [[atom]]s together. | ||
| + | : In an [[exothermic]] [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] [[energy]] is then released as [[atom]]s form new [[Chemical Bond|chemical bonds]]. | ||
| + | : In an [[exothermic]] [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] more [[energy]] is released in the formation of new [[Chemical Bond|bonds]] in the [[product]] than is taken in in the breaking of [[Chemical Bond|bonds]] in the [[reactant]]s. So there is a net output of [[energy]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | ====Higher==== | ||
| + | '''Example 1''' | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:StructuralDiagramMethane+Oxygen.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |In the [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] between [[Methane]] and [[Oxygen]] the [[Chemical Bond|chemical bonds]] in the [[reactant]]s must be broken first before the [[Chemical Bond|bonds]] in the [[product]]s are formed. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:100px; text-align:center;" |'''Bond''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Energy in kJ/mol''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:100px; text-align:center;" |C-H | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |413 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:100px; text-align:center;" |O=O | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |498 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:100px; text-align:center;" |O-H | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |464 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:100px; text-align:center;" |C=O | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |799 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are 4 C-H [[Chemical Bond|bonds]] and 2 O=O [[Chemical Bond|bonds]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4 x 413 + 2 x 498 = 2648kJ | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore 2648kJ/mol are needed to break the [[Chemical Bond|bonds]] in the [[reactant]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are 2 C=O [[Chemical Bond|bonds]] and 4 O-H [[Chemical Bond|bonds]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2 x 799 + 4 x 464 = 3454kJ | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore 3454kJ/mol is released when the [[Chemical Bond|bonds]] in the [[product]]s form. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once the [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] is complete 806kJ will be released. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Example 2''' | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:StructuralDiagramHydrogen+Nitrogen.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |In the [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] between [[Hydrogen]] and [[Nitrogen]] the [[Chemical Bond|chemical bonds]] in the [[reactant]]s must be broken first before the [[Chemical Bond|bonds]] in the [[product]]s are formed. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:100px; text-align:center;" |'''Bond''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |'''Energy in kJ/mol''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:100px; text-align:center;" |H-H | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |436 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:100px; text-align:center;" |N≡N | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |941 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:100px; text-align:center;" |N-H | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:150px; text-align:center;" |391 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are 3 H-H [[Chemical Bond|bonds]] and 1 N≡N [[Chemical Bond|bonds]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3 x 436 + 1 x 941 = 2249kJ | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore 2249kJ/mol are needed to break the [[Chemical Bond|bonds]] in the [[reactant]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are 6 N-H [[Chemical Bond|bonds]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6 x 391 = 2346kJ | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore 2346kJ/mol is released when the [[Chemical Bond|bonds]] in the [[product]]s form. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once the [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] is complete 97kJ will be released. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158762/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158762&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a0fffa35b3ea49a63404f6704e0df7cc ''Exothermic reaction, pages 173-5, 178-81, 211,216-7, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359373/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359373&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=952a73bbb09d222ecc4b50d200679849 ''Exothermic reactions, page 134, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=5ec5fc3f6429e30c1d9ab9bca2bccf93 ''Exothermic reactions, page 165, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945954/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945954&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=100574c08fbbb64318256eb79ed61a76 ''Exothermic reactions, page 179, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Exothermic reactions, page 61, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Exothermic reactions, pages 106, 231-2, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Exothermic reactions, pages 112-113, 114-119, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Exothermic reactions, pages 129-30, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Exothermic reactions, pages 152, 154, 155, 157, 159, 182-184, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Exothermic reactions, pages 177, 179, 180, 182, 184, 214-216, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d121 ''Exothermic reactions, pages 61-63, 72, 73, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Exothermic reactions; reaction profiles, pages 233, 235, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158754/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158754&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=27ad53b0283feeff7fc5ae04a9e205f283 ''Exothermic, page 36-7, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Exothermic; reaction profiles, page 131, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120207/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120207&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=22455ff53961978667722edaa64c0be5 ''Exothermic reactions, page 170, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948120/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948120&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=dedef775c6a43dbb0a609441525adac0 ''Exothermic reactions, page 270, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Exothermic reactions, pages 118, 252, 258-259, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Exothermic reactions, pages 134, 136, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Exothermic reactions, pages 138, 144-145, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Exothermic reactions, pages 243, 244, 248-250, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Exothermic reactions, pages 83, 85, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Exothermic reactions; equilibrium, page 239, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Exothermic reactions; equilibrium, page 95, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945660/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945660&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=83aa4500ad7759e7f401a1c5ba5df758 ''Exothermic reactions, page 20, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945679/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945679&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a2db42f7b4bdf10cafaafa3bb9120940 ''Exothermic reactions, page 41, 42, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359810/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359810&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=d768d99f1a06f7c12fab40e5aef85a55 ''Exothermic reactions, page 41, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359829/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359829&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=90e8d7b4f039d53035238fa0320fe00b ''Exothermic reactions, pages 102-103, 105, 186, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Exothermic reactions, pages 18, 111, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:50, 7 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
An exothermic process is one that gives out energy. This usually causes surroundings to increase in temperature.
About Exothermic Processes
- Most chemical reactions are exothermic with means they release energy to the environment and this is observed by an increase in temperature.
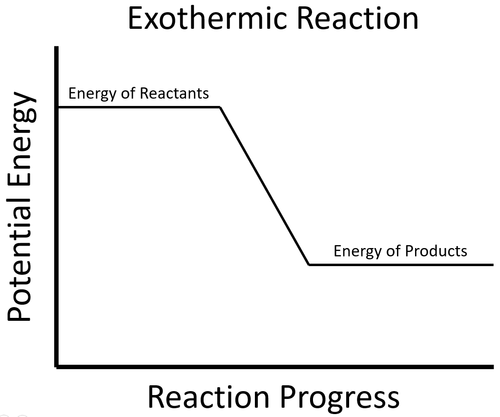
| The energy stored in the reactants is released in the chemical reaction making the material increase in temperature. The products now have less energy than the reactants. |
- Freezing, Condensing and Depositing are exothermic changes because they release energy when they happen. The material has less energy after they have happened. However, there is usually no increase in temperature because the material is usually cooled to change state because the surroundings are colder than the material during this process.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
An exothermic process is one that gives out energy. This usually causes surroundings to increase in temperature.
About Exothermic Processes
Foundation
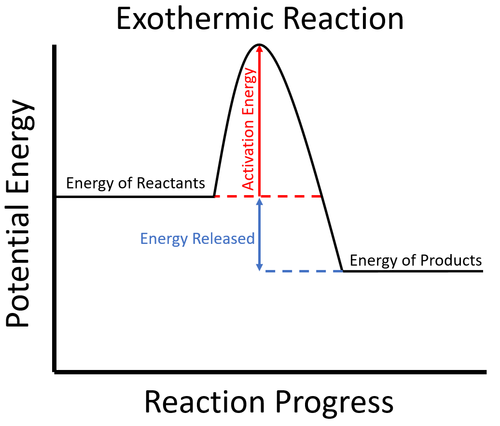
- Exothermic reactions usually require energy to begin. This is called the activation energy.
- In an exothermic process the potential energy stored in the products is less than the potential energy stored in the reactants.
| To start the reaction an activation energy is needed. This is usually achieved by initially heating the reactants. Once the reaction starts the energy stored in the reactants is released in the chemical reaction making the material increase in temperature. The products now have less energy than the reactants. |
Higher
- In a chemical reaction energy is needed to break the chemical bonds holding the atoms together.
- In an exothermic reaction energy is then released as atoms form new chemical bonds.
- In an exothermic reaction more energy is released in the formation of new bonds in the product than is taken in in the breaking of bonds in the reactants. So there is a net output of energy.
Examples
Higher
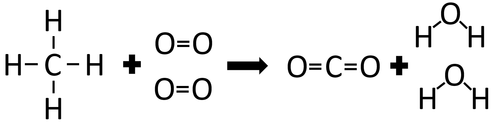
Example 1
| In the reaction between Methane and Oxygen the chemical bonds in the reactants must be broken first before the bonds in the products are formed. |
| Bond | Energy in kJ/mol |
| C-H | 413 |
| O=O | 498 |
| O-H | 464 |
| C=O | 799 |
There are 4 C-H bonds and 2 O=O bonds.
4 x 413 + 2 x 498 = 2648kJ
Therefore 2648kJ/mol are needed to break the bonds in the reactants.
There are 2 C=O bonds and 4 O-H bonds.
2 x 799 + 4 x 464 = 3454kJ
Therefore 3454kJ/mol is released when the bonds in the products form.
Once the reaction is complete 806kJ will be released.
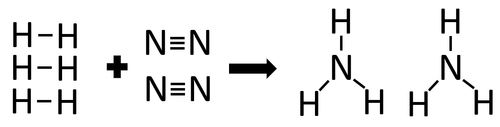
Example 2
| In the reaction between Hydrogen and Nitrogen the chemical bonds in the reactants must be broken first before the bonds in the products are formed. |
| Bond | Energy in kJ/mol |
| H-H | 436 |
| N≡N | 941 |
| N-H | 391 |
There are 3 H-H bonds and 1 N≡N bonds.
3 x 436 + 1 x 941 = 2249kJ
Therefore 2249kJ/mol are needed to break the bonds in the reactants.
There are 6 N-H bonds.
6 x 391 = 2346kJ
Therefore 2346kJ/mol is released when the bonds in the products form.
Once the reaction is complete 97kJ will be released.
References
AQA
- Exothermic reaction, pages 173-5, 178-81, 211,216-7, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Exothermic reactions, page 134, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Exothermic reactions, page 165, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Exothermic reactions, page 179, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Exothermic reactions, page 61, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Exothermic reactions, pages 106, 231-2, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Exothermic reactions, pages 112-113, 114-119, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Exothermic reactions, pages 129-30, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Exothermic reactions, pages 152, 154, 155, 157, 159, 182-184, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Exothermic reactions, pages 177, 179, 180, 182, 184, 214-216, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Exothermic reactions, pages 61-63, 72, 73, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Exothermic reactions; reaction profiles, pages 233, 235, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Exothermic, page 36-7, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Exothermic; reaction profiles, page 131, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Exothermic reactions, page 170, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Exothermic reactions, page 270, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Exothermic reactions, pages 118, 252, 258-259, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Exothermic reactions, pages 134, 136, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Exothermic reactions, pages 138, 144-145, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Exothermic reactions, pages 243, 244, 248-250, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Exothermic reactions, pages 83, 85, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Exothermic reactions; equilibrium, page 239, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Exothermic reactions; equilibrium, page 95, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
OCR
- Exothermic reactions, page 20, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Exothermic reactions, page 41, 42, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Exothermic reactions, page 41, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Exothermic reactions, pages 102-103, 105, 186, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Exothermic reactions, pages 18, 111, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR