Difference between revisions of "Titration"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== Titration is an experimental technique used to measure the exact volumes of acid and ...") |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
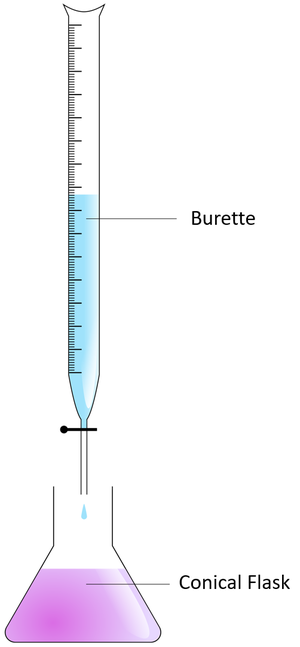
| − | [[Titration]] is an | + | [[File:Titration.png|right|300px|thumb|A [[diagram]] showing the setup for a [[titration]].]] |
| + | [[Titration]] is an experimental technique used to [[measure]] the exact [[Volume (Space)|volume]]s of [[acid]] and [[alkali]] needed to have a complete [[Neutralisation]] [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Titration=== | ||
| + | : During a [[titration]] one of the [[solution]]s is a fixed [[Volume (Space)|volume]] and the other is is added as needed and [[measure]]d as [[precision|precisely]] and [[accuracy|accurately]] as possible. | ||
| + | : To obtain a fixed [[Volume (Space)|volume]] a [[Volumetric Pipette]] is used. | ||
| + | : To [[measure]] the [[Volume (Space)|volume]] being added a [[Burette]] is used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Method=== | ||
| + | For a fixed [[Volume (Space)|volume]] of [[alkali]] and a [[measure]]d [[Volume (Space)|volume]] of [[acid]]. | ||
| + | #Wash the [[Volumetric Pipette|volumetric pipette]] and [[burette]] with [[Distilled Water|distilled water]] then wash the [[Volumetric Pipette|volumetric pipette]] with the [[alkali]] and the [[burette]] with the [[acid]] to avoid contamination from previous [[experiment]]s. | ||
| + | #Measure and record a fixed [[Volume (Space)|volume]] of [[alkali]] using the [[Volumetric Pipette|volumetric pipette]]. | ||
| + | #Add the [[alkali]] to a [[Conical Flask|conical flask]] and then add a few drops of [[pH Indicator]]. | ||
| + | #Fill the [[burette]] with [[acid]]. | ||
| + | #Add the [[acid]] to the [[alkali]] one drip at a time, swirling the [[Conical Flask|conical flask]] constantly to mix the [[reactant]]s thoroughly. | ||
| + | #Repeat until the [[pH Indicator]] shows the [[solution]] is [[Neutral (Chemistry)|neutral]]. | ||
| + | #Record the [[Volume (Space)|volume]] of [[acid]] added to the [[Conical Flask|conical flask]]. | ||
| + | #Repeat the [[experiment]] at least 3 times to produce an [[Mean Average|average]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158762/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158762&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a0fffa35b3ea49a63404f6704e0df7cc ''Titration, pages 97, 105, 118-9, 150-1, 282, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158762/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158762&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a0fffa35b3ea49a63404f6704e0df7cc ''Titration; curve, pages 118, 150, 153, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Titrations, pages 134, 135, 149-151, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d260 ''Titrations, pages 47, 51, 52, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Titrations, pages 74-77, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Titrations, pages 88-90, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Titrations, page 109, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Titrations, page 65, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Titrations, pages 131, 185, 186, 204, 205, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Titrations, pages 47, 65, 69, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Titrations; calculations, pages 114-115, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359829/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359829&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=90e8d7b4f039d53035238fa0320fe00b ''Titrations, pages 116-169, 274-275, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945679/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945679&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a2db42f7b4bdf10cafaafa3bb9120940 ''Titrations, pages 43, 64, 81, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:16, 20 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Titration is an experimental technique used to measure the exact volumes of acid and alkali needed to have a complete Neutralisation reaction.
About Titration
- During a titration one of the solutions is a fixed volume and the other is is added as needed and measured as precisely and accurately as possible.
- To obtain a fixed volume a Volumetric Pipette is used.
- To measure the volume being added a Burette is used.
Method
For a fixed volume of alkali and a measured volume of acid.
- Wash the volumetric pipette and burette with distilled water then wash the volumetric pipette with the alkali and the burette with the acid to avoid contamination from previous experiments.
- Measure and record a fixed volume of alkali using the volumetric pipette.
- Add the alkali to a conical flask and then add a few drops of pH Indicator.
- Fill the burette with acid.
- Add the acid to the alkali one drip at a time, swirling the conical flask constantly to mix the reactants thoroughly.
- Repeat until the pH Indicator shows the solution is neutral.
- Record the volume of acid added to the conical flask.
- Repeat the experiment at least 3 times to produce an average.
References
AQA
- Titration, pages 97, 105, 118-9, 150-1, 282, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Titration; curve, pages 118, 150, 153, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Titrations, pages 134, 135, 149-151, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Titrations, pages 47, 51, 52, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Titrations, pages 74-77, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Titrations, pages 88-90, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Titrations, page 109, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Titrations, page 65, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Titrations, pages 131, 185, 186, 204, 205, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Titrations, pages 47, 65, 69, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Titrations; calculations, pages 114-115, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel