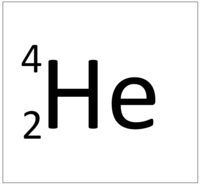Difference between revisions of "Atomic Number"
(→Key Stage 5) |
(→Examples) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
*Denoted by the symbol Z. | *Denoted by the symbol Z. | ||
*Defines the identity of an [[element]] (e.g., [[hydrogen]] has Z = 1). | *Defines the identity of an [[element]] (e.g., [[hydrogen]] has Z = 1). | ||
| − | *[[Element]]s in the [[Periodic Table|periodic table]] are ordered by increasing [[atomic number]]. | + | *[[Element]]s in the [[Periodic Table|periodic table]] are ordered by increasing [[Atomic Number|atomic number]]. |
*The [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] determines the [[element]]'s position in the [[Periodic Table|periodic table]]. | *The [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] determines the [[element]]'s position in the [[Periodic Table|periodic table]]. | ||
*The number of [[proton]]s is equal to the number of [[electron]]s in a [[Neutral Charge|neutral]] [[atom]]. | *The number of [[proton]]s is equal to the number of [[electron]]s in a [[Neutral Charge|neutral]] [[atom]]. | ||
| − | *The [[atomic number]] is unique for each [[element]] and distinguishes one [[element]] from another. | + | *The [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] is unique for each [[element]] and distinguishes one [[element]] from another. |
*Changes in the [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] result in the formation of different [[element]]s through [[Nuclear Reaction|nuclear reactions]]. | *Changes in the [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] result in the formation of different [[element]]s through [[Nuclear Reaction|nuclear reactions]]. | ||
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
| − | *[[Carbon]] has an [[atomic number]] of 6. | + | *[[Carbon]] has an [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] of 6. |
| − | *The [[atomic number]] of [[uranium]] is 92. | + | *The [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] of [[uranium]] is 92. |
Latest revision as of 19:35, 19 May 2024
Contents
Key Stage 3
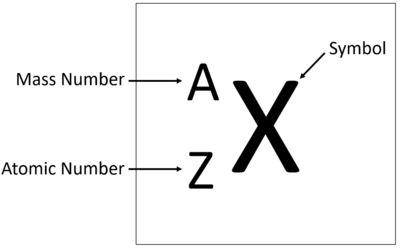
Meaning
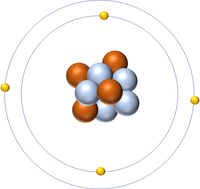
The Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
About The Atomic Number
- The Atomic Number of an atom determines which element it is.
- The number of protons also determines the number of electrons.
Examples
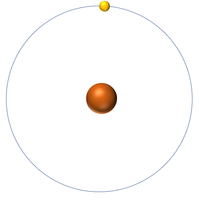
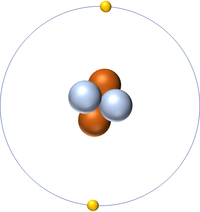
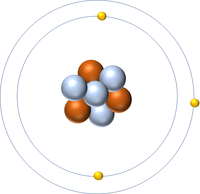
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
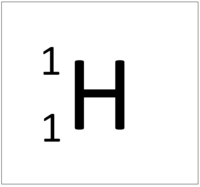
| Hydrogen has 1 proton so its atomic number is 1. | Helium has 2 protons so its atomic number is 2. | Lithium has 3 protons so its atomic number is 3. | Beryllium has 4 protons so its atomic number is 4. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
About The Atomic Number
- The Atomic Number of an atom determines which element it is.
- Protons have a relative atomic charge of +1 so the number of protons determines the relative atomic charge of the atomic nucleus.
- The number of electrons orbiting the nucleus is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Examples
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
| Hydrogen has 1 proton so its atomic number is 1 and the relative atomic charge of the nucleus is +1. | Helium has 2 protons so its atomic number is 2 and the relative atomic charge of the nucleus is +2. | Lithium has 3 protons so its atomic number is 3 and the relative atomic charge of the nucleus is +3. | Beryllium has 4 protons so its atomic number is 4 and the relative atomic charge of the nucleus is +4. |
References
AQA
- Atomic number (Z), page 89, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Atomic number, page 111, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Atomic number, page 123, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Atomic number, page 3-4, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Atomic number, page 44, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Atomic number, pages 119, 339, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Atomic numbers, page 96, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Atomic numbers, pages 12, 13, 22, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Atomic numbers, pages 14, 16, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Atomic numbers, pages 25, 52, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Atomic numbers, pages 25, 52, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Atomic numbers, pages 96, 97, 107, 198, 199, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Atomic; number, pages 109, 111, 116-17, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
Edexcel
- Atomic (proton) number, pages 79, 174, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Atomic (proton), number, page 51, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Atomic number, page 20, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Atomic number, page 92, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Atomic number, pages 164, 356, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Atomic number; periodic table, pages 172-173, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Atomic number; periodic table, pages 28-29, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Atomic numbers, page 16, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Atomic numbers, pages 35, 36, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
OCR
Key Stage 5
Meaning
The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, determining the chemical properties of an element.
About the Atomic Number
- Denoted by the symbol Z.
- Defines the identity of an element (e.g., hydrogen has Z = 1).
- Elements in the periodic table are ordered by increasing atomic number.
- The atomic number determines the element's position in the periodic table.
- The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
- The atomic number is unique for each element and distinguishes one element from another.
- Changes in the atomic number result in the formation of different elements through nuclear reactions.
Examples
- Carbon has an atomic number of 6.
- The atomic number of uranium is 92.