Difference between revisions of "Negative Ion"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Negative ions, pages 39, 188-189, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Negative ions, pages 39, 188-189, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Negative ions, pages 72, 258-261, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Negative ions, pages 72, 258-261, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Negative ions, tests for, pages 198-199, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359829/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359829&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=90e8d7b4f039d53035238fa0320fe00b ''Negative ions (anions0, pages 56-57, 88, 122, 125, 150-151, 272-273, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:41, 15 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
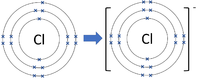
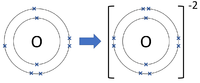
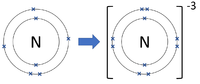
Negative ions are elements or compounds which have gained one or more electrons to become negatively charged.
About Negative Ions
- In chemical reactions between metals and non-metals the non-metal elements form negative ions.
- In alkalis there are free moving hydroxide ions which are negative ions. The concentration of these OH- ions is what determines the alkalinity of a solution.
- Negative ions are attracted to positive ions and to the positive electrode (anode) during electrolysis.
Examples
| Chlorine forms -1 ions. | Oxygen forms -2 ions. | Nitrogen forms -3 ions. |
References
AQA
- Negative ion, testing, page 263, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Negative ions, page 70, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Negative ions, pages 39, 188-189, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Negative ions, pages 72, 258-261, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA