Chlorine
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Chlorine is a Group 7 element, on the Periodic Table, with an atomic number of 17.
About Chlorine
Molecular Structure
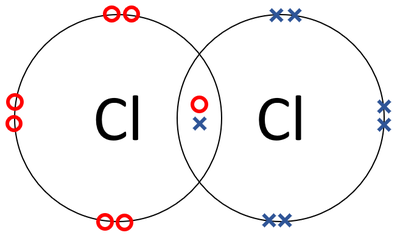
- Chlorine has the chemical formula Cl2.
Atomic Structure
- Chlorine as 17 protons and 18 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an Atomic Number of 17 and an atomic mass of 35.
- An atom of Chlorine is missing one electron from having a full outer shell.
Properties
- Chlorine is a non-metal element.
- Chlorine is a more reactive Halogen than Bromine but less reactive than Fluorine.
- Chlorine reacts strongly with Hydrogen to produce Hydrogen Chloride which dissolves in water to produce Hydrochloric Acid.
- Chlorine is a strong bleaching agent.
- Chlorine kills bacteria.
- Chlorine is a pale green coloured gas at room temperature.
Key Stage 4
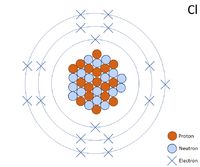
A 2 dimensional representation of the Bohr Model of a Chlorine-35 isotope with 17 protons and 18 neutrons in the nucleus and 2 electrons in the first shell, 8 in the second and 7 in the outer shell.
Meaning
Chlorine is a Group 7 element, on the Periodic Table, with 17 protons in the nucleus.
About Chlorine
Molecular Structure
- Chlorine has the chemical formula Cl2.
- Chlorine atoms join together in a covalent bond.
| A dot and cross diagram of a Chlorine molecule. |
Atomic Structure
- There are two stable isotopes of Chlorine, one with 18 neutrons and the other with 20 neutrons. They occur in a ratio of roughly 3:1 so the atomic mass of Chlorine is 35.5.
| Chlorine has two common stable Isotopes; Chlorine-35 and Chlorine-37. Chlorine-35 is three times more common than Chlorine-37 so the ratio is 3:1. Find the average atomic mass of Chlorine. |
| 1. State the known quantities.
Ratio: 3:1 3xChlorine-35 : 1xChlorine-37 |
| 2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
To find the average\[Average=\frac{35+35+35+37}{4}\] \(Average=\frac{35 \times 3 + 37 \times 1}{4}\) \(Average=35.5\) So the Relative Atomic Mass of Chlorine is quoted as 35.5 on the Periodic Table. |
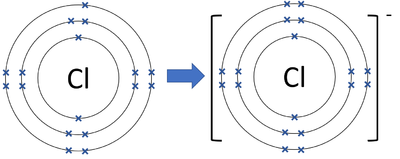
- An atom of Chlorine is missing one electron from having a full outer shell.
- Chloride ions gain 1 electron to get a full outer shell and become negatively charged.
| A diagram showing the formation of a Chloride ion. |
Properties
- Chlorine is a non-metal element.
- Chlorine is a more reactive Halogen than Bromine but less reactive than Fluorine.
- Chlorine reacts strongly with Hydrogen to produce Hydrogen Chloride which dissolves in water to produce Hydrochloric Acid.
- Chlorine is a strong bleaching agent.
- Chlorine kills bacteria.
- Chlorine is a pale green coloured gas at standard temperature and pressure.
Testing For Chlorine
- Collect the gas in a test tube.
- Place a piece of litmus paper over the mouth of the test tube.
- If the litmus paper is bleached white then the gas is Chlorine or Fluorine.
References
AQA
- Chlorine, identification of, page 207, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Chlorine, page 61, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Chlorine, page 61, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Chlorine, pages 102, 109, 185, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Chlorine, pages 15, 44-5, 64-5, 96, 165, 326, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Chlorine, pages 153, 163, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Chlorine, pages 88, 102, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Chlorine, test for, pages 160, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Chlorine; test for, page 203, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Chlorine; test for, page 257, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Chlorine; test, page 273, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA