Group 7
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
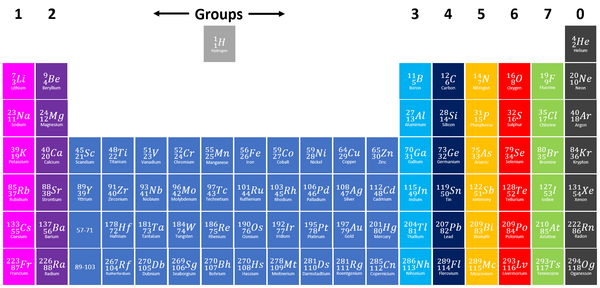
Group 7 elements, also known as Halogens on the Periodic Table are the elements which have 7 electrons in their outer shell.
| Group 7 elements are shown in green at the right of the Periodic Table. |
About the Halogens
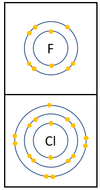
- The Halogens have similar chemical properties because they all have 7 electrons on their outer shell.
- Halogens all produce ions with a -1 relative charge because they gain an electron in chemical reactions.
The Halogens in order from most reactive to least reactive are:
Chemical Properties
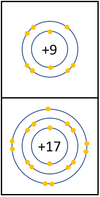
- The reactivity of Halogens decreases as you go down the Periodic Table.
- Halogens all react strongly as bleaching agents.
- Halogens all produce acids when combined with Hydrogen.
- Halogens are toxic to bacteria and are used in disinfectants.
| In a chemical reaction an extra electron is added to the outer shell.
The reactivity decreases as you go down the group because:
|
Physical Properties
The physical properties of Halogens changes significantly as you go down the Periodic Table:
- Fluorine - A yellow gas at room temperature.
- Chlorine - A green gas at room temperature.
- Bromine - A brown liquid at room temperature.
- Iodine - A purple solid at room temperature.
- Astatine -A dark purple solid at room temperature.
- The density, melting point and boiling point all increase as you go down the Periodic Table.
References
AQA
- Group 7 (halogens), pages 131-4, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Group 7 (halogens), pages 44-5, 46, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Group 7, page 110, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Group 7, page 25, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Group 7, pages 16-18, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Group 7, pages 28-29, 31, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Group 7, pages 61-63, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Group 7, pages 61-63, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Halogens, page 110, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Halogens, pages 131-4, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Halogens, pages 16-18, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Halogens, pages 25, 79, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Halogens, pages 28-29, 31, 158, 188-189, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Halogens, pages 44-5, 46, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Halogens, pages 61-63, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Halogens, pages 61-63, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Halogens; reaction with alkenes, pages 178-9, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Group 7, pages 20, 74, 75, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Group 7, pages 40, 49, 213-215, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Group 7, pages 83, 124, 125, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Halogens, pages 124, 125, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Halogens, pages 130-131, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Halogens, pages 244-245, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Halogens, pages 40, 49, 214-217, 277, 278, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Halogens, pages 74, 75, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Halogens; reactivity, pages 132-133, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Halogens; reactivity, pages 246-247, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
OCR
- Group 7 (IUPAC Group 17) elements, pages 70, 71, 86, 125, 134-137, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Group 7, pages 122, 123, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Group 7, pages 52, 53, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR