Iodine
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Iodine is a Group 7 element, on the Periodic Table, with an atomic number of 53.
About Iodine
Molecular Structure
- Iodine has the chemical formula I2.
Atomic Structure
- Iodine as 53 protons and 74 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an Atomic Number of 53 and an atomic mass of 127.
- An atom of Iodine is missing one electron from having a full outer shell.
Properties
- Iodine is a non-metal element.
- Iodine is a more reactive Halogen than Astatine but less reactive than Bromine.
- Iodine reacts with Hydrogen to produce Hydrogen Iodide which dissolves in water to produce Hydroiodic Acid.
- Iodine is a mild bleaching agent.
- Iodine kills bacteria.
- Iodine is a purple solid at room temperature.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Iodine is a Group 7 element, on the Periodic Table, with 53 protons in the nucleus.
About Iodine
Molecular Structure
- Iodine has the chemical formula I2.
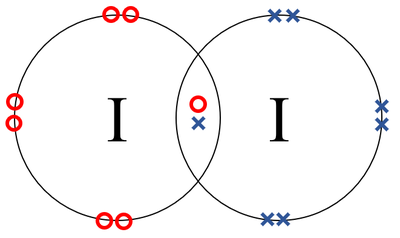
- Iodine atoms join together in a covalent bond.
| A dot and cross diagram of a Iodine molecule. |
Atomic Structure
- The most stable isotope of Iodine has 74 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an atomic mass of 127.
- An atom of Iodine is missing one electron from having a full outer shell.
- Iodine ions gain 1 electron to get a full outer shell and become negatively charged.
Properties
- Iodine is a non-metal element.
- Iodine is a more reactive Halogen than Astatine but less reactive than Bromine.
- Iodine reacts strongly with Hydrogen to produce Hydrogen Iodide which dissolves in water to produce Hydroiodic Acid.
- Iodine is a mild bleaching agent.
- Iodine kills bacteria.
- Iodine is a brown coloured gas at standard temperature and pressure.