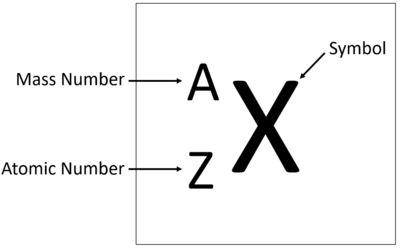
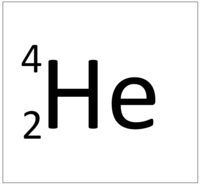Difference between revisions of "Atomic Number"
(→Examples) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
: [[Proton]]s have a [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative atomic charge]] of +1 so the number of [[proton]]s determines the [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative atomic charge]] of the [[Atomic Nucleus|atomic nucleus]]. | : [[Proton]]s have a [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative atomic charge]] of +1 so the number of [[proton]]s determines the [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative atomic charge]] of the [[Atomic Nucleus|atomic nucleus]]. | ||
: The number of [[electron]]s [[orbit]]ing the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] is the same as the number of [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] of an [[atom]]. | : The number of [[electron]]s [[orbit]]ing the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] is the same as the number of [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] of an [[atom]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Hydrogen''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Helium''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Lithium''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Beryllium''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:Hydrogen.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:Helium.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:Lithium.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:Beryllium.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:HydrogenSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:HeliumSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:LithiumSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:BerylliumSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
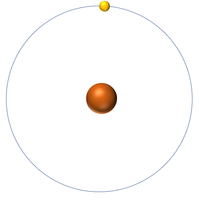
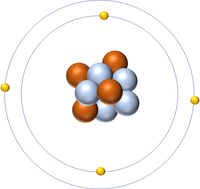
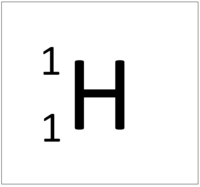
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Hydrogen]] has 1 [[proton]] so its '''atomic number''' is 1 and the [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative atomic charge]] of the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] is +1. | ||
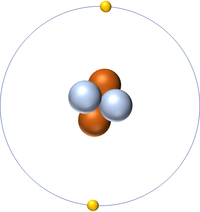
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Helium]] has 2 [[proton]]s so its '''atomic number''' is 2 and the [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative atomic charge]] of the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] is +2. | ||
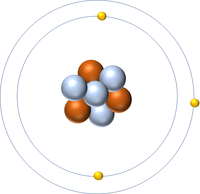
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Lithium]] has 3 [[proton]]s so its '''atomic number''' is 3 and the [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative atomic charge]] of the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] is +3. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Beryllium]] has 4 [[proton]]s so its '''atomic number''' is 4 and the [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative atomic charge]] of the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] is +4. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Atomic number (Z), page 89, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Atomic number, page 111, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Atomic number, page 123, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Atomic number, page 3-4, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac25 ''Atomic number, page 44, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Atomic number, pages 119, 339, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Atomic numbers, page 96, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d48 ''Atomic numbers, pages 12, 13, 22, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Atomic numbers, pages 14, 16, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Atomic numbers, pages 25, 52, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Atomic numbers, pages 25, 52, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09699 ''Atomic numbers, pages 96, 97, 107, 198, 199, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Atomic; number, pages 109, 111, 116-17, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Atomic (proton) number, pages 79, 174, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Atomic (proton), number, page 51, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Atomic number, page 20, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Atomic number, page 92, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Atomic number, pages 164, 356, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Atomic number; periodic table, pages 172-173, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Atomic number; periodic table, pages 28-29, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Atomic numbers, page 16, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Atomic numbers, pages 35, 36, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945679/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945679&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a2db42f7b4bdf10cafaafa3bb9120940 ''Atomic (proton) number, pages 15, 16, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR Gateway ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 5== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | The [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] is the number of [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] of an atom, determining the chemical properties of an [[element]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About the Atomic Number=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Denoted by the symbol Z. | ||
| + | *Defines the identity of an [[element]] (e.g., [[hydrogen]] has Z = 1). | ||
| + | *[[Element]]s in the [[Periodic Table|periodic table]] are ordered by increasing [[Atomic Number|atomic number]]. | ||
| + | *The [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] determines the [[element]]'s position in the [[Periodic Table|periodic table]]. | ||
| + | *The number of [[proton]]s is equal to the number of [[electron]]s in a [[Neutral Charge|neutral]] [[atom]]. | ||
| + | *The [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] is unique for each [[element]] and distinguishes one [[element]] from another. | ||
| + | *Changes in the [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] result in the formation of different [[element]]s through [[Nuclear Reaction|nuclear reactions]]. | ||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | *[[Carbon]] has an [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] of 6. | ||
| + | *The [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] of [[uranium]] is 92. | ||
Latest revision as of 19:35, 19 May 2024
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
The Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
About The Atomic Number
- The Atomic Number of an atom determines which element it is.
- The number of protons also determines the number of electrons.
Examples
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
| Hydrogen has 1 proton so its atomic number is 1. | Helium has 2 protons so its atomic number is 2. | Lithium has 3 protons so its atomic number is 3. | Beryllium has 4 protons so its atomic number is 4. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
About The Atomic Number
- The Atomic Number of an atom determines which element it is.
- Protons have a relative atomic charge of +1 so the number of protons determines the relative atomic charge of the atomic nucleus.
- The number of electrons orbiting the nucleus is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Examples
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
| Hydrogen has 1 proton so its atomic number is 1 and the relative atomic charge of the nucleus is +1. | Helium has 2 protons so its atomic number is 2 and the relative atomic charge of the nucleus is +2. | Lithium has 3 protons so its atomic number is 3 and the relative atomic charge of the nucleus is +3. | Beryllium has 4 protons so its atomic number is 4 and the relative atomic charge of the nucleus is +4. |
References
AQA
- Atomic number (Z), page 89, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Atomic number, page 111, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Atomic number, page 123, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Atomic number, page 3-4, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Atomic number, page 44, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Atomic number, pages 119, 339, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Atomic numbers, page 96, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Atomic numbers, pages 12, 13, 22, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Atomic numbers, pages 14, 16, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Atomic numbers, pages 25, 52, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Atomic numbers, pages 25, 52, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Atomic numbers, pages 96, 97, 107, 198, 199, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Atomic; number, pages 109, 111, 116-17, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
Edexcel
- Atomic (proton) number, pages 79, 174, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Atomic (proton), number, page 51, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Atomic number, page 20, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Atomic number, page 92, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Atomic number, pages 164, 356, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Atomic number; periodic table, pages 172-173, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Atomic number; periodic table, pages 28-29, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Atomic numbers, page 16, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Atomic numbers, pages 35, 36, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
OCR
Key Stage 5
Meaning
The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, determining the chemical properties of an element.
About the Atomic Number
- Denoted by the symbol Z.
- Defines the identity of an element (e.g., hydrogen has Z = 1).
- Elements in the periodic table are ordered by increasing atomic number.
- The atomic number determines the element's position in the periodic table.
- The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
- The atomic number is unique for each element and distinguishes one element from another.
- Changes in the atomic number result in the formation of different elements through nuclear reactions.
Examples
- Carbon has an atomic number of 6.
- The atomic number of uranium is 92.