Difference between revisions of "GCSE Physics Required Practical: Investigating Hooke's Law"
(→Method) |
(→Improving Accuracy) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
====Improving [[Accuracy]]==== | ====Improving [[Accuracy]]==== | ||
| − | : Calculate the [[weight]] added by [[measure|measuring]] its [[mass]] each time and using the equation <math>W=mg</math> with <math>g=9.8</math>. This will give a more [[accuracy|accurate]] knowledge of the [[weight]] rather than relying on the number printed on the [[weight]]s. | + | : Calculate the [[weight]] added by [[measure|measuring]] its [[mass]] using an [[Electronic Balance|electronic balance]] on a flat, level surface each time and using the equation <math>W=mg</math> with <math>g=9.8</math>. This will give a more [[accuracy|accurate]] knowledge of the [[weight]] rather than relying on the number printed on the [[weight]]s. |
: Add a [[Fiduciary Marker|fiduciary marker]] to the bottom of the [[Coil Spring|coil spring]] to prevent any [[error]] caused by not [[read]]ing the [[ruler]] from [[Eye Level|eye level]]. | : Add a [[Fiduciary Marker|fiduciary marker]] to the bottom of the [[Coil Spring|coil spring]] to prevent any [[error]] caused by not [[read]]ing the [[ruler]] from [[Eye Level|eye level]]. | ||
: Ensure the [[Coil Spring|spring]] is not moving when taking [[measure]]ments of it's length. | : Ensure the [[Coil Spring|spring]] is not moving when taking [[measure]]ments of it's length. | ||
Revision as of 15:29, 20 March 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Investigate the relationship between the extension of a spring and the force applied to that spring.
Experiment
Variables
- Independent Variable: The force applied to the spring.
- Dependent Variable: The extension of the spring.
- Control Variables: The spring being used.
Method
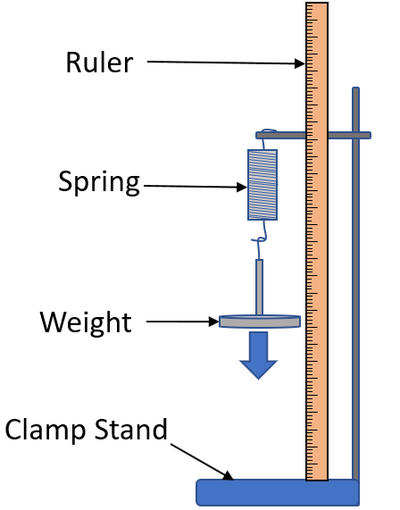
| A diagram of the apparatus used to investigate the effect of a force on the extension of a spring. |
- Set up the equipment as shown in the diagram.
- Measure the original length of the spring using a ruler.
- Attach a known weight (approximately 1N) to the spring.
- Measure the new length of the spring.
- Calculate the extension of the spring by subtracting the original length from the new length of the spring.
- Repeat steps 2-4 up to around 6N.
- Plot a scatter graph with the force of weight on the y-axis and the extension on the x-axis. The gradient of line of best fit will be the spring constant of the coil spring.
Improving Accuracy
- Calculate the weight added by measuring its mass using an electronic balance on a flat, level surface each time and using the equation \(W=mg\) with \(g=9.8\). This will give a more accurate knowledge of the weight rather than relying on the number printed on the weights.
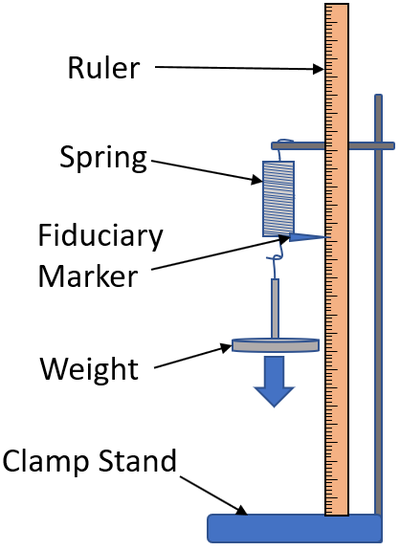
- Add a fiduciary marker to the bottom of the coil spring to prevent any error caused by not reading the ruler from eye level.
- Ensure the spring is not moving when taking measurements of it's length.
| A fiduciary marker can be added to improve accuracy and precision of the length measurements. |
Improving Precision
- Calculate the weight correct to two significant figures by measuring its mass to two significant figures each time and using the equation \(W=mg\) with \(g=9.8\). This will give a more precise knowledge of the weight rather than relying on the number printed on the weights which may be precise to only one significant figure.
- Add a fiduciary marker with a fine point to the bottom of the coil spring to give a precise reading of the length of the coil spring.