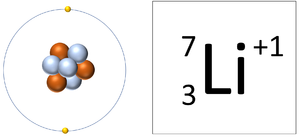Difference between revisions of "Relative Atomic Charge"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== '''Relative Atomic Charge''' is the charge of a particle compared to the charge of a single proton. ===About Relative Atomic Cha...") |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
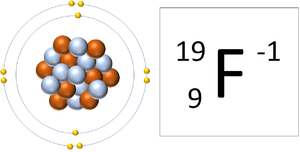
: The [[charge]] on an [[ion]] is shown at the top right of the [[element]] symbol: | : The [[charge]] on an [[ion]] is shown at the top right of the [[element]] symbol: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|[[File:LithiumIon+Symbol.png|center|300px]] | |[[File:LithiumIon+Symbol.png|center|300px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 21:11, 25 November 2018
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Relative Atomic Charge is the charge of a particle compared to the charge of a single proton.
About Relative Atomic Charge
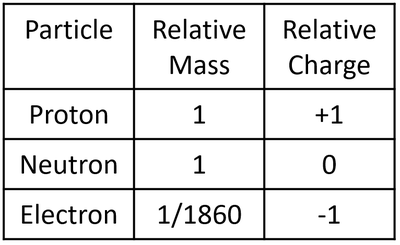
- Ions, nuclei and subatomic particles have extremely small charges such as the proton (1.6x10-19Coulombs) so instead of stating the charge in Coulombs it is compared to the charge of a proton.
| A table showing the relative mass and relative charge of the proton, neutron and electron. |
| A Lithium ion has 3 protons and 2 electrons so it has a positive charge. It now has a full Outer Shell. |
| A Fluorine atom has 9 protons and 10 electrons so it is negative charge. It now has a full Outer Shell. |