Difference between revisions of "State of Matter"
(→About States of Matter) |
(→About States of Matter) |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Property''' | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Property''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
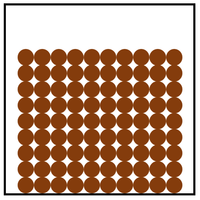
| − | |rowspan=" | + | |rowspan="5"|[[File:ParticleModelSolid.png|center|200px]] |
|rowspan="2"|[[Particle]]s are in fixed positions. | |rowspan="2"|[[Particle]]s are in fixed positions. | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Solid]]s hold their shape. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Solid]]s hold their shape. | ||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Property''' | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Property''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
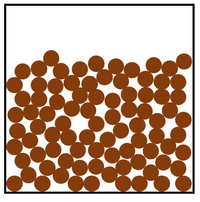
| − | |rowspan=" | + | |rowspan="6"|[[File:ParticleModelLiquid.png|center|200px]] |
|rowspan="3"|[[Particle]]s can slide past each other. | |rowspan="3"|[[Particle]]s can slide past each other. | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Liquid]]s can be poured. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Liquid]]s can be poured. | ||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Property''' | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Property''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
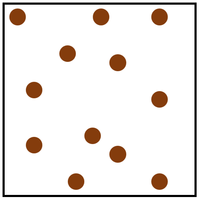
| − | |rowspan=" | + | |rowspan="6"|[[File:ParticleModelGas.png|center|200px]] |
|rowspan="3"|[[Particle]]s are free to move in all directions. | |rowspan="3"|[[Particle]]s are free to move in all directions. | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Gas]]es fit the size of their container. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Gas]]es fit the size of their container. | ||
Revision as of 19:08, 21 December 2018
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
State of matter means whether a material is solid, liquid or gas.
About States of Matter
- Materials can be solid, liquid or gas.
- The state of matter can be changed by heating or cooling the material.
- Heating can turn a solid into a liquid. This is called melting.
- Heating can turn a liquid to a gas. This is called evaporating.
- Cooling can turn a gas into a liquid. This is called condensing.
- Cooling can turn a liquid into solid. This is called freezing.
| Brick is a solid material. | Water is a liquid material. | Inside the balloon is a gas called helium. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
State of matter means whether a material is solid, liquid or gas.
About States of Matter
- Materials can be solid, liquid or gas.
- The state of matter can be changed by heating or cooling the material.
- Heating can turn a solid into a liquid by melting or it can turn a solid straight into a gas by subliming.
- Heating can turn a liquid to a gas. This is called evaporating.
- Cooling can turn a gas into a liquid by condensing or it can turn a gas into a solid by depositing.
- Cooling can turn a liquid into solid. This is called freezing.
| This diagram shows the 3 states of matter in the particle model. |
Properties of the States of Matter
| Solid | Liquid | Gas |
| Cannot be compressed. | Cannot be compressed. | Can be compressed. |
| Does not flow. | Can flow. | Can flow. |
| Holds its shape. | Fits the shape of the container. | Fits the size and shape of the container. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
State of matter means whether a material is solid, liquid or gas.
About States of Matter
- Materials can be solid, liquid or gas.
- The state of matter can be altered by changing the temperature of the material or changing the pressure on the material.
| Particle Diagram | Particle Arrangement | Property |
| Particles are in fixed positions. | Solids hold their shape. | |
| Convection cannot happen in solids. | ||
| Particles are very close together. | Solids cannot be compressed. | |
| Sound passes through solids faster than liquids and gases. | ||
| Particles vibrate. | Thermal Conduction happens best in solids. |
| Particle Diagram | Particle Arrangement | Property |
| Particles can slide past each other. | Liquids can be poured. | |
| Liquids fit the shape of their container. | ||
| Convection happens in solids. | ||
| Particles and close together. | Liquids cannot be compressed. | |
| Sound passes through liquids faster than gases. | ||
| Thermal Conduction happens in liquids but not as well as in solids. |
| Particle Diagram | Particle Arrangement | Property |
| Particles are free to move in all directions. | Gases fit the size of their container. | |
| Gases fit the shape of their container. | ||
| Convection happens most easily in gases. | ||
| Particles are spread apart. | Gases can be compressed into a smaller volume. | |
| Sound passes through gases slower than liquids and solids. | ||
| Thermal Conduction is very poor in a gases. |