Difference between revisions of "Boron"
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
: [[Boron]] is a [[metalloid]] [[element]] so in some conditions it is an [[Electrical Conductor|electrical conductor]]. | : [[Boron]] is a [[metalloid]] [[element]] so in some conditions it is an [[Electrical Conductor|electrical conductor]]. | ||
: [[Boron]] is a shiny [[solid]] at [[STP|standard temperature and pressure]] and has a high [[Melting Point|melting point]]. | : [[Boron]] is a shiny [[solid]] at [[STP|standard temperature and pressure]] and has a high [[Melting Point|melting point]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Boron, page 129, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 12:06, 28 October 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Key Stage 3
Meaning
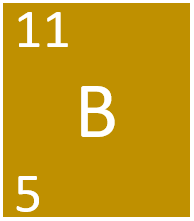
Boron is a Group 3 metalloid element, on the Periodic Table, with an atomic number of 5.
About Boron
- Boron has the chemical symbol B.
Atomic Structure
- Boron as 5 protons and 6 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an Atomic Number of 5 and an atomic mass of 11.
- Boron is in Period 2 of the Periodic Table because it has 2 electron shells.
Properties
- Boron is a shiny solid at room temperature.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Boron is a Group 3 metalloid element, on the Periodic Table, with 5 protons in the nucleus.
About Boron
- Boron has the chemical symbol B.
Atomic Structure
- The most stable isotope of Boron has 6 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an atomic mass of 11.
- Boron is in Period 2 of the Periodic Table because it has 2 electron shells.
- Boron loses electrons to form positive metal ions.
Properties
- Boron is a metalloid element so in some conditions it is an electrical conductor.
- Boron is a shiny solid at standard temperature and pressure and has a high melting point.