Difference between revisions of "Boron"
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
: [[Boron]] is a shiny [[solid]] at [[STP|room temperature]]. | : [[Boron]] is a shiny [[solid]] at [[STP|room temperature]]. | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
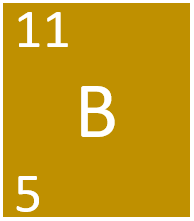
| + | [[File:BKS4.PNG|right|300px|thumb|The [[Chemical Symbol|chemical symbol]] for [[Boron]].]] | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
[[Boron]] is a [[Group 3]] [[metalloid]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with 5 [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | [[Boron]] is a [[Group 3]] [[metalloid]] [[element]], on the [[Periodic Table]], with 5 [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | ||
Revision as of 10:49, 29 February 2020
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Boron is a Group 3 metalloid element, on the Periodic Table, with an atomic number of 5.
About Boron
- Boron has the chemical symbol B.
Atomic Structure
- Boron as 5 protons and 6 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an Atomic Number of 5 and an atomic mass of 11.
- Boron is in Period 2 of the Periodic Table because it has 2 electron shells.
Properties
- Boron is a shiny solid at room temperature.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Boron is a Group 3 metalloid element, on the Periodic Table, with 5 protons in the nucleus.
About Boron
- Boron has the chemical symbol B.
Atomic Structure
- The most stable isotope of Boron has 6 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an atomic mass of 11.
- Boron is in Period 2 of the Periodic Table because it has 2 electron shells.
- Boron loses electrons to form positive metal ions.
Properties
- Boron is a metalloid element so in some conditions it is an electrical conductor.
- Boron is a shiny solid at standard temperature and pressure and has a high melting point.