Difference between revisions of "Chromatography"
(→About Chromatography) |
(→Key Stage 4) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
*[[Separating Mixtures|Separating]] separating [[liquid]]s in [[solution]] - [[Fractional Distillation]] | *[[Separating Mixtures|Separating]] separating [[liquid]]s in [[solution]] - [[Fractional Distillation]] | ||
*[[Separating Mixtures|Separating]] an [[insoluble]] [[solid]] from a [[soluble]] [[solid]] - [[Filtration]] | *[[Separating Mixtures|Separating]] an [[insoluble]] [[solid]] from a [[soluble]] [[solid]] - [[Filtration]] | ||
| − | *[[Separating Mixtures|Separating]] [[solute]]s from a [[solvent]] in [[solution]]. - [[Evaporation of | + | *[[Separating Mixtures|Separating]] [[solute]]s from a [[solvent]] in [[solution]]. - [[Evaporation of Solutions|Evaporation (Crystallisation)]] or [[Distillation]]. |
Revision as of 11:53, 22 January 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Chromatography is a method used to separate and identify different solutes found in a solution.
About Chromatography
- When more than one solute is dissolved in a solvent chromatography can be used to separate them.
- Chromatography experiments are often done with colourful solutes which can be seen easily.
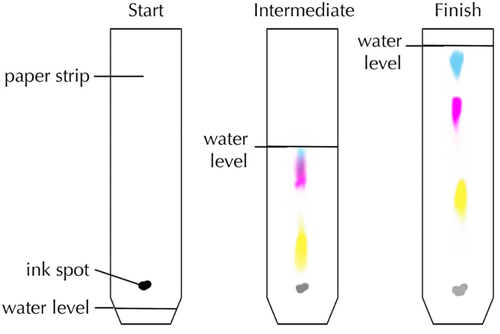
| This diagram shows how black ink is made of three different inks in solution. |
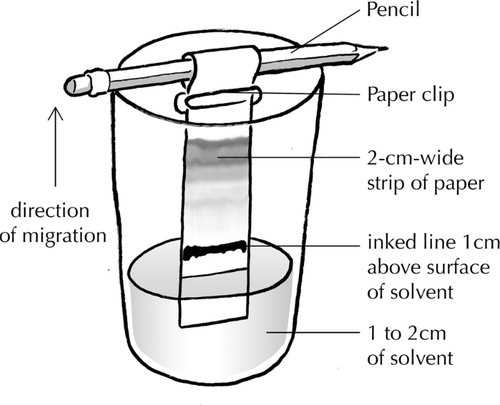
Method
|
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Chromatography is a technique used to separate and identify different solutes found in a solution.
About Chromatography
Chromatography is only be used for:
- Separating and identifying two or more solutes from a solution.
Chromatography cannot be used for:
- Separating separating liquids in solution - Fractional Distillation
- Separating an insoluble solid from a soluble solid - Filtration
- Separating solutes from a solvent in solution. - Evaporation (Crystallisation) or Distillation.