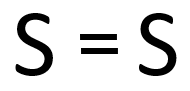Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A double bond is a chemical bond in which two electrons are shared or transferred from the outer shell between two atoms.
About Double Bonds
- In covalent bonds a double bond means two electrons from the outer shell of an atom are shared with another atom.
- In ionic bonds a double bond means one of the elements has gained or lost two electrons from/to one other element.
Examples
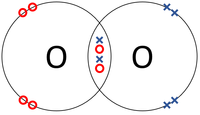
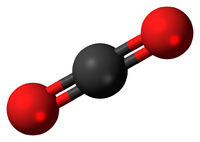
| In this structural diagram a double bond is shown between two Sulphur atoms. | In this dot and cross diagram the two Oxygen atoms in an Oxygen molecule are shown to each share two electrons in a double bond. | In this ball and stick model of Carbon Dioxide the Carbon is shown to share two electron (shown by the two sticks) with each Oxygen atom forming two double bonds. |
References
AQA
- Double bonds, pages 154-155, 158-159, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Double bonds, pages 230-237, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Double bonds, pages 78-80, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA