Dissolving
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Dissolving is when a solid is placed in a liquid and it is broken down into tiny pieces that can't be seen.
About Dissolving
- Dissolving is a reversible process.
- When something dissolves the solid cannot be seen anymore.
- If a coloured solid dissolves the water will turn that colour.
| Brown sugar is a soluble solid. | Brown sugar can dissolve in water. | The solid cannot be seen anymore because it has dissolved. The solution is now the colour of the brown sugar. |
Note to Teachers
Students often confuse dissolving for melting. It is important to make sure they have active experiences of both so that they can understand the distinction. Melting ice, melting wax. Dissolving sugar, dissolving salt, dissolving coloured jelly crystals.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Dissolving is when a solid breaks apart into individual molecules or atoms when it is mixed with a liquid.
About Dissolving
- When a solid is dissolved it cannot be seen anymore because it has been broken down into pieces too small to see, even with a microscope.
- The Particle Model can be used to explain the process of dissolving.
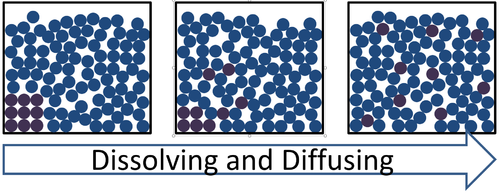
| This particle diagram shows the particles in a purple solid becoming separated from one another and spreading through the liquid from a high concentration to a low concentration. |
- Not all solids can dissolve in water. A solid which can be dissolved easily in water is described as soluble but one that cannot be easily dissolved in water is described as insoluble.
- A solid that has dissolved in a liquid is called a solute and the liquid is called a solvent.
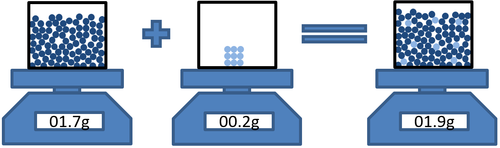
- Conservation of Mass can be shown when a solute dissolves in a solvent the total mass of the solution is the same as the total mass of the parts that made it.
| Masssolvent + Masssolute = Masssolution |
Factors That Affect Dissolving
- The time it takes to dissolve a solid can be decreased by stirring the solution and by keeping the solution at a higher temperature.
- The amount of solid which can be dissolved can be increased by keeping the solution at a higher temperature.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Dissolving is an endothermic process in which a solid breaks apart into individual molecules or atoms when it is mixed with a liquid.
About Dissolving
- A solid that has dissolved in a liquid is called a solute and the liquid is called a solvent.
- Dissolving is an endothermic process, which means it needs to absorb energy to take place. This means that when a solid dissolves in a liquid the temperature of the liquid decreases.
- Dissolving is a physical change, which means it is reversible and does not produce new chemicals.
- Different substances have a different level of solubility. The more of a substance which can be dissolved in a fixed volume of liquid, the greater its solubility.
- Some solids can be dissolved in ethanol or oil but not in water. Fats can be dissolved in ethanol but not in water. Vitamin D can be dissolved in oil but not in water.