Difference between revisions of "Electron Orbital"
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Electron shells; outer, page 184, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Electron shells; outer, page 184, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Electron shells; outer, page 40, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Electron shells; outer, page 40, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945679/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945679&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a2db42f7b4bdf10cafaafa3bb9120940 ''Electron shells, pages 13, 14, 16, 17, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Electron shells, pages 21, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Electron shells, pages 84, 87, 88, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:29, 5 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
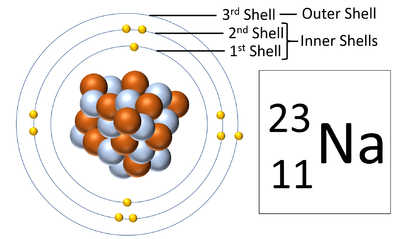
Electron shells are the places around a nucleus where an electron can orbit the nucleus.
| A diagram of a Sodium atom shown the electron shells. |
About Electron Shells
- The number of electron shells is shown by the period on the Periodic Table.
- The number of electrons in the outer shell determines the chemical properties of the element.
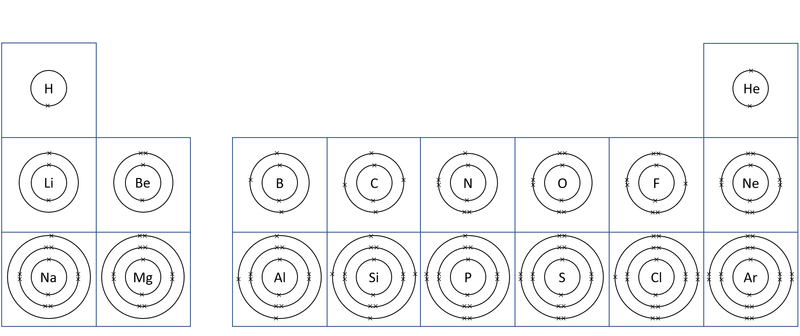
| A diagram of the first 20 elements in the Periodic Table showing the electron shells. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
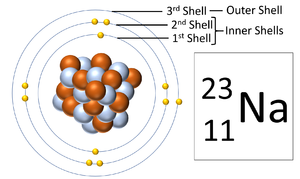
Electron orbitals, also known as an electron shells, are the locations where electrons orbit the nucleus of atoms.
About Electron Orbitals
- Each electron orbital only holds a certain number of electrons.
- These orbitals and the number of electrons in an atom determine the chemistry of an element.
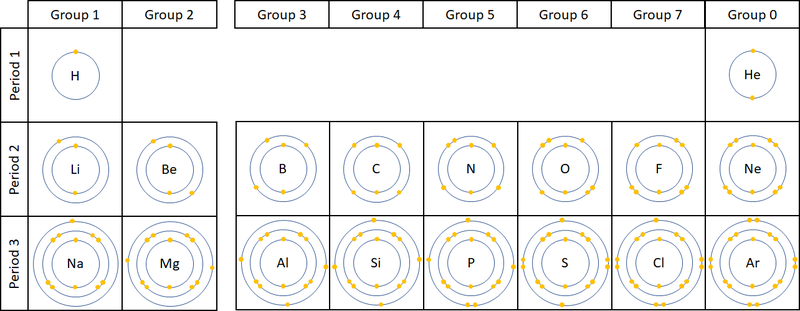
- The number of electron orbitals determines the Period on the Periodic Table.
- The number of electrons in the last orbital (Outer Shell) determines the Group on the Periodic Table.
| A diagram showing the electron shells and electrons in the first 20 elements on the Periodic Table. NB Group 0 used to be called Group 8 but this caused confusion because most elements in Group 8 have 8 electrons in their Outer Shell but Helium only has 2, so it was renamed Group 0. |
- Atoms in the same group have similar chemical properties because they all have the same number of electrons in their Outer Shell.
References
AQA
Edexcel
- Electron shells, page 94, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Electron shells, pages 16, 18, 19, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Electron shells, pages 162, 174, 358, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Electron shells, pages 18, 30, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Electron shells, pages 33, 35, 42, 43, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Electron shells; outer, page 184, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Electron shells; outer, page 40, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel