Group (Chemistry)
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
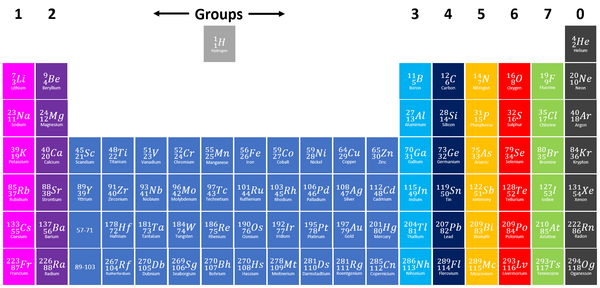
A Group is a column on the Periodic Table with elements with the same number of electrons on the Outer Shell.
About Groups
- Helium, in Group 0 is an exception to this rule as it has 2 electrons in its Outer Shell.
- The elements are arranged groups of similar chemical properties.
- Elements have similar chemical properties when they have the same number of electrons in the Outer Shell.
Trends within groups
The chemical properties of elements within a group are similar. However, the reactivity within a group changes as you move up or down the periods.
- Group 1: The Alkali Metals all react strongly with water. The reactivity increases as you go down the group.
- Group 2: The Alkali Earth Metals all react strongly with steam and acids. The reactivity increases as you go down the group.
- Group 7: The Halogens all act as bleaching agents and kill bacteria. The reactivity decreases as you go down the group.
- Group 0: The Noble Gases are all inert (unreactive).
The physical properties of elements within a group are similar. However, the property changes gradually as you move down the group.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A Group is a column on the Periodic Table with elements with the same number of electrons on the Outer Shell.
About Groups
- Helium, in Group 0 is an exception to this rule as it has 2 electrons in its Outer Shell.
- The elements were oringally arranged groups of similar chemical properties.
- It was later discovered that elements have similar chemical properties when they have the same number of electrons in their Outer Shells.
Trends within groups
The chemical properties of elements within a group are similar. However, the reactivity within a group changes as you move up or down the periods due to the number of Electron Shells.
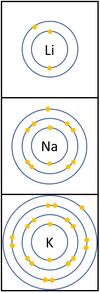
Group 1: The Alkali Metal
Chemical Properties
- Alkali Metals are all highly reactive and will oxidise quickly in the presence of Oxygen.
- Alkali Metals all react strongly with water to produce metal hydroxides and Hydrogen gas.
- Alkali Metals all produce strong alkalis.
| In a chemical reaction the electron in the outer shell is lost.
The reactivity increases as you go down the group because:
|
Physical Properties
- Alkali Metals have a low density compared to other metals.
- Alkali Metals are all solid at room temperature but have a low melting point compared to other metals.
- Alkali Metals are soft and can be easily cut.
- Alkali Metals all appear shiny (before they oxidise).
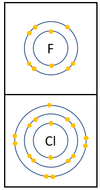
Group 7: The Halogens
Chemical Properties
- The reactivity of Halogens decreases as you go down the Periodic Table.
- Halogens all react strongly as bleaching agents.
- Halogens all produce acids when combined with Hydrogen.
- Halogens are toxic to bacteria and are used in disinfectants.
| In a chemical reaction an extra electron is added to the outer shell.
The reactivity decreases as you go down the group because:
|
Physical Properties
The physical properties of Halogens changes significantly as you go down the Periodic Table:
- Fluorine - A yellow gas at room temperature.
- Chlorine - A green gas at room temperature.
- Bromine - A brown liquid at room temperature.
- Iodine - A purple solid at room temperature.
- Astatine -A dark purple solid at room temperature.
- The density, melting point and boiling point all increase as you go down the Periodic Table.
Group 0: The Noble Gases
Chemical Properties
- The Nobel Gases are all inert (unreactive) because they have a full outer shell.
Physical Properties
- The Nobel Gases are all gases at room temperature.
- The density and boiling point all increase as you go down the Periodic Table.
References
Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table), page 173, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table), page 29, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); group 0 elements, pages 134-135, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); group 0 elements, pages 248-249, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); group 1 elements, pages 128-129, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); group 1 elements, pages 242-243, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); group 7 elements, pages 130-131, 132-133, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); group 7 elements, pages 244-245, 246-247, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); valency, page 185, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Groups (of the periodic table); valency, page 41, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Groups (periodic table), pages 81-83, 123, 124, 126, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Groups, pages 18-20, 73, 74, 76, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel