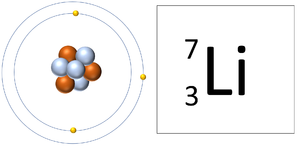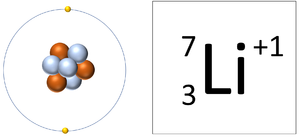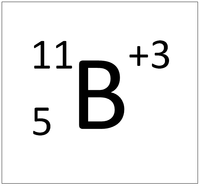Difference between revisions of "Ion"
(→About Ions) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A [[Fluorine]] [[atom]] has 9 [[proton]]s and 9 [[electron]]s so it is [[Neutral Charge|neutral]]. | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A [[Fluorine]] [[atom]] has 9 [[proton]]s and 9 [[electron]]s so it is [[Neutral Charge|neutral]]. | ||
| style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A [[Fluorine]] [[ion]] has 9 [[proton]]s and 10 [[electron]]s so it is [[Negative Charge|negative charge]]. It now has a full [[Outer Shell]]. | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A [[Fluorine]] [[ion]] has 9 [[proton]]s and 10 [[electron]]s so it is [[Negative Charge|negative charge]]. It now has a full [[Outer Shell]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | : The number of [[electron]] in an [[ion]] can be found using the [[Atomic Number]] (which is the same as the [[Relative Atomic Charge]] of the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]) and subtracting the [[charge]] of the [[ion]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''A Lithium Ion''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''A Fluorine Ion''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''A Boron Ion''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''An Oxygen Ion ''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:LithiumIonSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
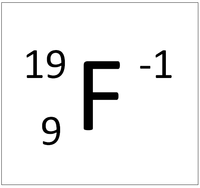
| + | |[[File:FluorineIonSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:BoronIonSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
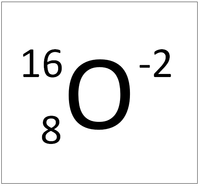
| + | |[[File:OxygenIonSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |This [[atom]] has an [[Atomic Number]] (Z) of 1 and a [[Relative Atomic Mass]] (A) of 1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Number of [[neutron]]s = A - Z | ||
| + | |||
| + | Number of [[neutron]]s = 1 - 1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Number of [[neutron]]s = 0 | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |This [[atom]] has an [[Atomic Number]] (Z) of 2 and a [[Relative Atomic Mass]] (A) of 4. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Number of [[neutron]]s = A - Z | ||
| + | |||
| + | Number of [[neutron]]s = 4 - 2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Number of [[neutron]]s = 2 | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |This [[atom]] has an [[Atomic Number]] (Z) of 3 and a [[Relative Atomic Mass]] (A) of 7. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Number of [[neutron]]s = A - Z | ||
| + | |||
| + | Number of [[neutron]]s = 7 - 3 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Number of [[neutron]]s = 4 | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |This [[atom]] has an [[Atomic Number]] (Z) of 4 and a [[Relative Atomic Mass]] (A) of 9. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Number of [[neutron]]s = A - Z | ||
| + | |||
| + | Number of [[neutron]]s = 9 - 4 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Number of [[neutron]]s = 5 | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 14:35, 26 November 2018
Key Stage 4
Meaning
An Ion is a particle that has a different number of protons to electrons.
About Ions
- An atom contains the same number of protons as electrons. When an atom loses or gains electrons it becomes an ion.
- Ions can be positively charged or negatively charged.
- If an atom gains electrons it becomes a negatively charged ion since there are more electrons than protons and electrons carry a negative charge.
- If an atom loses electrons it becomes a positively charged ion since there are more protons than electrons and protons carry a positive charge.
| Atom | Ion |
| A Lithium atom has 3 protons and 3 electrons so it is neutral. | A Lithium ion has 3 protons and 2 electrons so it has a positive charge. It now has a full Outer Shell. |
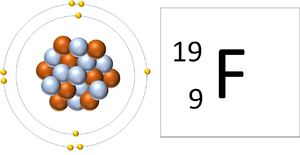
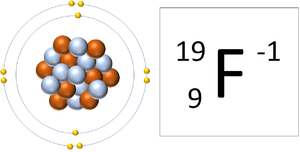
| A Fluorine atom has 9 protons and 9 electrons so it is neutral. | A Fluorine ion has 9 protons and 10 electrons so it is negative charge. It now has a full Outer Shell. |
- The number of electron in an ion can be found using the Atomic Number (which is the same as the Relative Atomic Charge of the nucleus) and subtracting the charge of the ion.
| A Lithium Ion | A Fluorine Ion | A Boron Ion | An Oxygen Ion |
| This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 1 and a Relative Atomic Mass (A) of 1.
Number of neutrons = A - Z Number of neutrons = 1 - 1 Number of neutrons = 0 |
This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 2 and a Relative Atomic Mass (A) of 4.
Number of neutrons = A - Z Number of neutrons = 4 - 2 Number of neutrons = 2 |
This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 3 and a Relative Atomic Mass (A) of 7.
Number of neutrons = A - Z Number of neutrons = 7 - 3 Number of neutrons = 4 |
This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 4 and a Relative Atomic Mass (A) of 9.
Number of neutrons = A - Z Number of neutrons = 9 - 4 Number of neutrons = 5 |